* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure of Physics
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Supersymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantum gravity wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chromodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum tunnelling wikipedia , lookup
Quantum gravity wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Matrix mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chaos wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
Peter Kalmus wikipedia , lookup
Quantum logic wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Theory of everything wikipedia , lookup
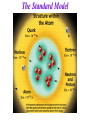
Overview of the Structure of Physics Where do Statistical &Thermal Physics fit in? Niels Bohr 1922 Nobel Prize in Physics for “His services in the investigation of the structure of atoms and of the radiation emanating from them.” Interesting Trivia (to me)! Neils Bohr is the Only Nobel Prize winner to have also been an Olympic Medalist! In the 1908 Olympics, he & his brother Harald* were on the Danish soccer team, which won a sliver medal! *Harald Bohr later became a world famous mathematician! The Structure of Physics Classical Physics is The Foundation of pure & applied (macroscopic) physics & engineering! Newton’s Laws + Electromagnetism + Statistical Mechanics + Thermodynamics. These give a good description of most of the macroscopic world. Classical Mechanics (Newton, Lagrange, Hamilton,..) The Physics of the 17th & 18th Centuries. Still useful in the 21st Century!! Physics Structure Classical Electromagnetism & Optics (Newton, Coulomb, Gauss, Faraday, Maxwell,..) The Physics of the 18th & 19th centuries. Still useful in the 21st Century! High Speeds (v ≤ ~ c) Special Relativity (Einstein, ..) 20th Century Physics! Small Size (atomic & smaller): Quantum Mechanics (Bohr, Schrödinger, Heisenberg….) 20th century physics! “Mechanics” • HOW objects move (behave) under given forces. • (Usually) Does not deal with the sources of forces. Answers the question: Given the forces, how do objects move? • Forces in the universe are classified into 4 types: The 4 Fundamental Forces Of Nature! Some version of Mechanics applies to all four! The 4 Fundamental Forces of Nature The sources of the forces, in order of decreasing strength The Strong Nuclear Force: Binds nuclei together. Explained by “Standard Model” & Quantum Chromodynamics. Still being researched. The Electromagnetic Force: E&M phenomena. Chemical forces. Most everyday forces. Maxwell, Coulomb, Ampere, Faraday, ... The Weak Nuclear Force: Nuclear decay. Fermi, Bethe, others. Electroweak Theory. The Gravitational Force: Newton (classical mechanics), Einstein (general relativity), Hawking…. The 4 Fundamental Forces of Nature The sources of the forces, in order of decreasing strength The Four Fundamental Forces The “Electro-Weak” Force Since ~ the late 1960’s, in some sense, the 4 fundamental forces have been reduced to three! That is, the Electromagnetic Force & the Weak Nuclear Force were combined into one theory. This was first done by S. Weinberg & A. Salaam. For this work, they received the 1972 Nobel Prize in Physics! The Standard Model of Particle Physics The “Periodic Table for Elementary Particles”! Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD) & the Electroweak Theory Protons & Neutrons consist of 3 Quarks each. The Standard Model The Standard Model The Standard Model SUMMARY: THE STRUCTURE OF PHYSICS Low Speed High Speed v << c v<~c Large size Classical Mechanics Special Relativity >> atomic size (Newton, Hamilton, (Einstein) Lagrange) Small size Quantum Mechanics < ~ atomic size (Schrodinger, Heisenberg) Atomic Physics Molecular Physics Solid State Physics Nuclear & Particle Physics Relativistic Quantum Mechanics (Dirac) Quantum Field Theory (Feynman, Schwinger) Quantum Electrodynamics (Photons, Weak Nuclear Force) Quantum Chromodynamics (Gluons, Quarks, Leptons Strong Nuclear Force) The Rest of Physics! • What we’ve mentioned so far is all of physics except: Statistical Mechanics: (This course ≡ “Stat Mech” ) “Stat Mech” is the mechanics of systems of huge numbers (>> ~ 1023) of particles. Statistical Mechanics 1. Uses Probability & Statistics to calculate macroscopic properties from microscopic force laws. 2. Applies to BOTH the Classical & the Quantum worlds! 3. Is the major link between microscopic & macroscopic physics! 4. Contains Thermodynamics as a sub-theory!