* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 PPT/Notes B
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electron-beam lithography wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
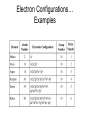
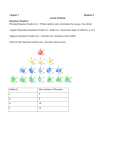
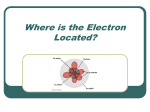
The Quantum Mechanical Model •By the mid-1920’s scientists were convinced that the Bohr model needed modification… •Louis de Broglie(1892-1987) proposed an idea to fix the energy levels for the Bohr model. •De Broglie proposed that all particles traveled as waves and proposed the wave formula for the electron orbits. (see p149) •Problem: What is the wavelength of an electron moving at 5.31 x 10 6 m/sec? Louis de Broglie De Broglie’s Electron Wave • Solution: de Broglie's equation is λ = h/mv λ = 6.626 x 10 -34 J·s/ 9.11 x 10 -31 kg x 5.31 x 10 6 m/sec λ = 6.626 x 10 -34 J·s/4.84 x 10 -24 kg·m/sec λ = 1.37 x 10 -10 m λ = 1.37 Å Answer: The wavelength of an electron moving 5.31 x 10 6 m/sec is 1.37 x 10 -10 m or 1.37 Å. De Broglie’s Electron Waves • The below pattern is of electrons passing through a single crystal . Bright spots are antinodal, dark spaces are nodal Electrons As Waves • A consequence of this theory are considerable paradoxes. Young's Double Slit experiment can and has been carried out with electrons, protons, neutrons and various molecules including C60 - "buckminsterfullerene" - that extraordinary form of carbon shaped as a soccer ball. • If single objects approach a double slit, they pass through and slowly build up, one by one, the double slit pattern. Shut one slit off and they, one by one, create the single slit diffraction pattern. Question: How do single "objects" "know" of the existence of two slits? "Clearly" they only pass through one slit! ( But if they only pass through one slit, why the two slit pattern.................HELP!!!) • http://www.launc.tased.edu.au/online/sciences/physics/d ebroglie.html • Young’s Slit Experiment Electrons as waves • Electrons can only make orbits with whole numbers of waves….. Electrons as Waves The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle • H.U.P states that you cannot know, with certainty, both the velocity and location of a moving particle. The Schrodinger Wave Equation • In 1926, Erwin Schrodinger developed the quantum mechanical model of the atom. • His model developed a ‘probable’ location for electrons mathematically. • Each electron can be described by quantum numbers…sub-levels and orbitals. Quantum Numbers 1. Principal quantum number = n… each major energy level is called a principal energy level… n also tells how many sub-levels are present… 1 for n=1, 2 for n=2, etc 2. Principal energy levels contain energy sublevels… s,p,d,f 3. Orbitals…s has 1 orbital, p has 3 orbitals, d has 5 orbitals, and f has 7 orbitals https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=accyCUzasa0 5.3 Electron Configurations • Use the Aufbau diagrams to build electron configurations. • Numbers represent principal energy levels • Letters s,p,d,f represent sub-levels • The superscript tells you electrons present in an orbital Ground-State • Ground-state configuration would be an atom at its lowest energy level. • We use 3 rules to write configurations… • The Aufbau principle says electrons fill the lowest energy levels first. • Hund’s rule says to place one electron in each orbital before placing the 2nd one of opposite spin. • The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that an atomic orbital can hold, at most, 2 electrons. • We use arrows to designate electrons… up for +1/2 and down for -1/2 spin. • Use your Aufbau diagram and fill using the 3 rules… for fluorine and neon…. Orbital Shapes(See p 158 ) For Neon Orbital Diagram Noble-Gas Configuration Notation • A short-cut for writing configurations would use brackets and the noble-gas symbol to designate start here and write the rest of the configuration Electron Configurations… Examples The Periodic Table and s,p,d,f Credits • UC Davis Science • http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/Physical_Chem istry/Quantum_Mechanics/Quantum_Theor y/De_Broglie_Wavelength • Bozeman Science https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=accyCU zasa0 • Matter and Change, McGraw Hill, chapter 5, p134-163.