* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Snímek 1
Dementia with Lewy bodies wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Excoriation disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Factitious disorder imposed on another wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar II disorder wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Rumination syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Emil Kraepelin wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antipsychotic wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Dementia praecox wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Sluggish schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
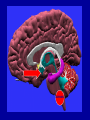
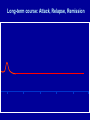
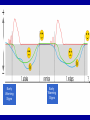
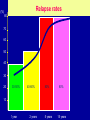
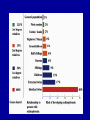
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders Symptoms, models, course, epidemiology Lucie Bankovská Motlová Psychotic Disorder – Psychotic: loss of contact with reality, inability to distinguish reality from fantasy, impaired reality testing, with the creation of a new reality – Characteristics: » disorganized and delusional thinking » disturbed perceptions » inappropriate emotions and actions substance-induced psychotic disorder schizoaffective PSYCHOSES disorder brief psychotic disorder schizophrenia schizophreniform disorder Psychotic Disorders: Classification Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM-IV • Schizophrenia • Schizophreniform disorder • Schizoaffective disorder • Delusional disorder • Brief psychotic disorder • Shared psychotic disorder • Psychotic disorder due to a general medical condition • Substance-induced psychotic disorder International Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems ICD-10 • Schizophrenia • Schizotypal disorder • Persistent delusional disorders • Acute and transient psychotic disorders • Induced delusional disorder • Schizoaffective disorders Schizophrenia John Nash Symptoms • Positive • Negative • Cognitive Positive Symptoms Auditory, Visual, Tactile,Olfactory Symptom Hallucinations Disorganized Speech Bizarre/catatonic behavior Delusions Persecutory, Paranoid, Grandiose, Religious, Jealous, Somatic Function Distorted Perception Thought/Language Behavioral monitoring Inferential thinking April 1991 Bryan Charnley 1949-1991 May 1991 Stefan M., Travis M. and Murray R., An Atlas of Schizophrenia, 2002 June 1991 Stefan M., Travis M. and Murray R., An Atlas of Schizophrenia, 2002 DOPAMIN Neurochemical sensitization in mesolimbic dopaminergic system (studies in schizophrenia) • Endogenous dopaminergic sensitization: PET • Amphetamines intake = ↑↑↑ endogenous dopamin in schizophrenia patients in the acute phase, in comparison with healthy persons • Relapse of schizophrenia = recurrence of hyperdopaminergic state in subcortical structures • IMPLICATIONS FOR TREATMENT Chronic blockade of D2 receptors: blocking of sensitization processes Laurelle 1999 Negative Symptoms Symptom Alogia Affective blunting Avolition Anhedonia Function Diminished Fluency of speech/thought Emotional expression Volition and drive Hedonic capacity Impair ability to function in daily life Holding a job Attending school Forming friendships Having intimate family relationships Cognitive Symptoms Symptom • forgetfullness • distractibility • reasoning/problem solving Function Diminished • working memory • Attention span • "set-shifting", i.e. the ability to display flexibility in the face of changing schedules of reinforcement Learning difficulties Inability to read Problems with planning Historical Concepts • Emil Kraepelin • Eugen Bleuler • Kurt Schneider Video: 1942 Emil Kraepelin (1856-1926) Dementia Praecox “Dementia praecox consists of a series of states, the common characteristic of which is a peculiar destruction of internal connections of the psychic personality....the majority of the clinical pictures are the expression of a single morbid process, though outwardly they often diverge very far from one another.” Eugen Bleuler (1857-1939): Group of Schizophrenias “Of the thousands of associative threads that guide our thinking, this disease seems to interrupt, quite haphazardly, sometimes single threads, sometimes a whole group, and sometimes whole segments of them.” Bleuler’s Fundamental Symptoms: 4 „A“ • • • • Associations Affective Blunting Autism Ambivalence Kurt Schneider (1887-1967) First-Rank Symptoms First-Rank Symptoms of Kurt Schneider • • • • • • • • • • Audible thoughts Voices arguing or discussing Voices commenting on patient´s actions Somatic passivity Thought withdrawal Thought broadcasting Made feelings Made impulses or drives Made volitional acts Delusional perception Syndromes, models, classification systems John Hughlins Jackson Timothy Crow ICD -10, DSM IV John Hughlins Jackson (1835-1911) Positive and negative symptoms Positive •Delusions, hallucinations •Pathological disinhibition of cortical functions •Absent in normal „psyche“ Negative •Flat affect, apathy, lack of motivation •Generalized loss of functions •Normal „psyche“ lost them Timothy Crow Schizophrenia type I and II I •Positive symptoms •Normal size of brain ventricules •Better prognosis •Better treatment response II •Negative symptoms •Brain ventricules enlargement •Worse prognosis •Worse treatment response Classification ICD-10 Europe; DSM-IV-USA • General criteria 1st rank symptoms according to Schneider • Long-term course types • Clinical subtypes Traditional clinical Subtypes • • • • Paranoid Disorganized (Hebephrenic) Catatonic Simplex • Undifferentiated • Residual Out of the Shadow What symptoms of schizophrenia have you identified? Course and prognosis of schizophrenia Long-term course: Attack, Relapse, Remission M 20 30 E D I K 40 A C 50 roky E 60 70 The natural history of schizophrenia: a 5-year follow-up. Early Warning Signs Early Warning Signs Early Warning Symptoms of Relapse Patient 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Troubles with sleep. Decreased appetite. Difficulty concentrating on reading or watching television. Fear, anxiety or annoying feelings from other people. Restlessness, irritability or quick temperedness. Feeling that something unusual and incomprehensible is about to happen around me. Loss of energy or interests. Decreased capacity to cope with everyday problems. Experience of hearing people's voices speaking when nobody seems to be around. Have you noticed any of your individual warning signs since last evaluation? Family member 1. Troubles with sleep. 2. Marked behavioral changes. 3. Social withdrawal. 4. Decline in daily activities. 5. Decline in personal hygiene. 6. Loss of initiative, motivation. 7. Preoccupation with peculiar ideas and thoughts. 8. Marked poverty of speech or content of speech. 9. Irritability, quick temperedness or aggression. 10. Have you noticed any of warning signs individual for your relative since last evaluation? Relapse rates (%) 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 30-50% 40-60% 80% 80% 10 1 year 2 years 5 years 15 years (Shepherd et al , 1989, Hogarty et al 1993, Möller et al., 1995, Wieden a Olfson 1995, Mason et al, WHO studie, 1996, Doering et al.,1998, Wiersma et al. 1998, Robinson et al. 1999, Ohmori et al . 1999, Rabinowitz et al. 2001, Gaebel 2002, Schooler et al., 2003) Epidemiology Onset and Prevalence of Schizophrenia worldwide About 0.2% to 1.5% (or about 1% population) Often develops in early adulthood Can emerge at any time Schizophrenia Is Generally Chronic Most suffer with moderate-to-severe lifetime impairment Life expectancy is less than average Schizophrenia Affects Males and Females About Equally Females tend to have a better long-term prognosis Onset differs between males and females Schizophrenia has a Strong Genetic Component