* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thyroid Disorders
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
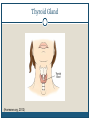
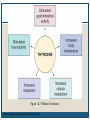
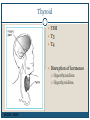
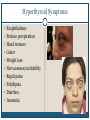
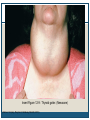
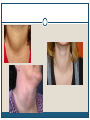
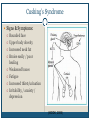
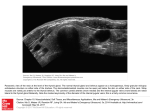
Thyroid Disorders Endocrine Glands Collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. Adrenal glands, parathyroid glands, pancreas, pineal gland, pituitary gland, ovaries, testes, thymus gland, thyroid gland Thyroid Gland (Hormone.org, 2012) Figure 12-7: Effects of thyroxine. (Zelman, Tompary, Raymond, Holdaway, Mulvhill, 2010) Thyroid TSH T3 T4 Disruption of hormones (NIDDK, 2006) Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism One of the most common hyperthyroid disorders Graves’ Disease More common in women than men Hyperthyroid Symptoms Exophthalmos Profuse perspiration Hand tremors Goiter Weight loss Nervousness/excitability Rapid pulse Polydipsia Diarrhea Insomnia Insert Figure 12-9: Thyroid goiter. (Newscom) (Zelman, Tompary, Raymond, Holdaway, Mulvhill, 2010) Hypothyroidism Most common type of hypothyroidism Hashimoto’s Disease The thyroid doesn’t make enough thyroid hormone Symptoms: Fatigue, mental depression, feeling cold, weight gain, dry skin and hair, constipation, menstrual irregularities Thyroid Cancer Most people have no symptoms 4 types: Papillary – slow growing – easily treated – rarely fatal Follicular – again slow growing – rarely fatal Medullary – less common – more aggressive Anaplastic – least common – most aggressive Addison’s Disease Adrenal Insufficiency Adrenal glands cannot produce enough cortisol • OR Pituitary gland fails to produce enouch adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) Symptoms: Chronic, worsening fatigue Muscle weakness Loss of appetite Weight loss Nausea/vomiting Diarrhea Craving for salty foods Low blood glucose Headache Cushing’s Syndrome Caused by prolonged exposure of the body’s tissues to high levels of the hormone cortisol. Relatively rare but risk factors: Obesity Type 2 diabetes High blood pressure Cushing’s Syndrome Signs & Symptoms: Rounded face Upper body obesity Increased neck fat Bruise easily / poor healing Weakened bones Fatigue Increased thirst/urination Irritability / anxiety / depression (NIDDK, 2006) Insert Figure 12-11: A patient with Cushing’s syndrome (A) before and (B) after receiving treatment. (Sharmyn McGraw) (Zelman, Tompary, Raymond, Holdaway, Mulvhill, 2010) Treatments Medication Radioactive Iodine Surgery Prevention??