* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
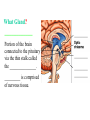
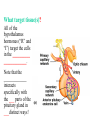
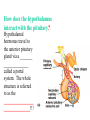
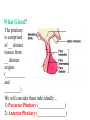
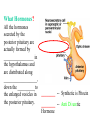
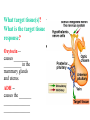
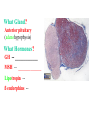
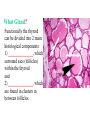
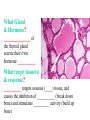
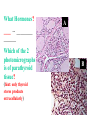
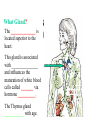
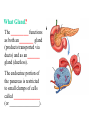
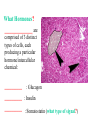
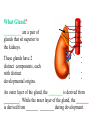
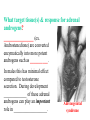
BIOL 2030 Human Anatomy & Physiology II What are the parts and how do they fit? Guiding questions for this chapter: _____________? _____________? ________________? _____________? _____________? What Gland? ________________ _________ Portion of the brain connected to the pituitary via the thin stalk called the _______________. _________ _________ is comprised of nervous tissue. _________ _________ What Hormones? All the hormones formed by the hypothalamus are either “R” releasing or “I” inhibiting. GHRH -- ______________________________ GHIH -- ______________________________ GnRH -- ______________________________ TRH -- ______________________________ CRH -- ______________________________ PRH -- ______________________________ PIH -- ______________________________ What target tissue(s)? All of the hypothalamus hormones (“R” and “I”) target the cells in the __________ _____________. Note that the _____________ interacts specifically with the ___ parts of the pituitary gland in ___distinct ways! What is the target tissue response? In response to the “R” and “I” hormones of the hypothalamus… Ex. ________________________ causes the secretion of _________________ How does the hypothalamus interact with the pituitary? Hypothalamal hormones travel to the anterior pituitary gland via a _______ ______________ called a portal system. The whole structure is referred to as the _________________ _______________!!! What Gland? The pituitary is comprised of __ distinct tissues from __ distinct origins (___________ and _________) We will consider them individually… 1) Posterior Pituitary (_______________) 2) Anterior Pituitary (________________) What Hormones? All the hormones secreted by the posterior pituitary are actually formed by _________________ in the hypothalamus and are distributed along ___________________, down the __________to the enlarged vesicles in ________ -- Synthetic is Pitocin the posterior pituitary. ________ -- Anti Di uretic Hormone What target tissue(s)? What is the target tissue response? Oxytocin -causes ________ __________ in the mammary glands and uterus. ADH -causes the _______ _______________ _______________ What Gland? _______________ (adenohypophysis) What Hormones? TSH -- ________________ ACTH -- ______________ LH -- __________________ FSH -- _______________ Prolactin -- ____________ ______________… cause secretion of OTHER hormones from ____________! What Gland? Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) What Hormones? GH -- _____________ MSH -- _____________ Lipotropin -- ß endorphins -- What target tissues & target tissue responses? GH MSH Lipotropin ß endorphins ACTH LH FSH Prolactin -- __________ --- ___________ --- ____________ --- ____ --- ____________ --- ____________ --- ____________ --- _____________-- What Gland? ____________ consists of 2 lobes joined by a narrow bridge (isthmus). Located inferior to the ________ and anterior to the __________. One of largest endocrine glands! What Gland? Functionally the thyroid can be divided into 2 main histological components: 1) ______________, which surround sacs (follicles) within the thyroid and 2) ______________, which are found in clusters in between follicles. ? ? Follicle What Hormones? Follicular cells secrete T3 (___________) and T4 (____________ or ___________) These hormones depend on_______ for their synthesis. They are bound with the protein ___________ inside the follicle. About 1-2 weeks worth stored in ________ and in _________. T3 & T4 released from thyroglobulin before release into bloodstream. What target tissues and target tissue responses? Targets = ____________ Response = What Gland & Hormone? _______________ of the thyroid gland secrete their own hormone: __________. ? What target tissue(s) & response? __________ targets osseous (____) tissue, and causes the inhibition of __________ (break down bone) and stimulates _________ activity (build up bone) Take 5!!! An enlargement of the thyroid (goiter) can develop from iodine deficiencies. Why does the thyroid gland respond by swelling? Discuss with your neighbor and predict an answer What diseases & disorders are related to too <>? * Symptoms? * Symptoms? What Gland? _____________ glands are comprised of __ __________ small glands embedded in the ____________ portion of the thyroid lobes. What Hormones? A ____ -- _________ _______ Which of the 2 photomicrographs is of parathyroid tissue? (hint: only thyroid stores products extracellularly) B What target tissue(s)? ________________________ are target organs for PTH. What is the target tissue response? ___ = _________ Antagonist to Calcitonin The response of all three types of organs is to attempt to ____________________________ (Ca2+ ). Osseous (bone) tissue responds with an elevated _______ (dissolve bone) activity and suppressed __________ (build bone) activity. ____________ and ________ increase re-absorption rate of Ca2+ from digested food and urine respectively. What Gland? The ______________ is located superior to the heart. This gland is associated Thymus with _______________ and influences the maturation of white blood cells called _______ via hormone __________. The Thymus gland ___________ with age. What Gland? The __________ functions as both an ________ gland (products transported via ducts) and as an _______ gland (ductless). The endocrine portion of the pancreas is restricted to small clumps of cells called _______________ (or _________________). What Hormones? ________________ are comprised of 3 distinct types of cells, each producing a particular hormone/intercellular chemical: __________ : Glucagon __________ : Insulin __________ : Somatostatin (what type of signal?) What target tissue(s) and responses? _________: __________ (except CNS) -- Causes cellular uptake of ______, ______ & ________ from blood. _________: primarily ______ -- Causes breakdown of ________. __________: _______ __________ of pancreas - __________________. What Gland? Adrenal gland __________ are a pair of glands that sit superior to the kidneys. These glands have 2 distinct components, each with distinct developmental origins. An outer layer of the gland, the ________ is derived from _________. While the inner layer of the gland, the _______ is derived from _______ ________ during development. What Hormones? The hormones secreted are specific to each region of the gland. Medulla: ____________ & _____________ Cortex has 3 subregions: _____________ : _______________ (ex. Androstenedione) _____________ : _______________ (ex. Cortisol) _____________ : _____________ (ex. Aldosterone) What target tissue(s) & response for epinephrine? Target tissues include the _______, ____ ______, ____ and _____. The response is an elevated ________, and _____, some vessels constrict while some dilate. What target tissue(s) & response for adrenal androgens? _________________ (ex. Androstenedione) are converted enzymatically into more potent androgens such as __________. In males this has minimal effect compared to testosterone secretion. During development _____________ of these adrenal androgens can play an important role in ___________________. Adrenogenital syndrome What target tissue(s) & response for glucocorticoids? _______________ (ex. _______) target many tissues including, _______, _______, _______, _____ & _________. The non-immune component’s responses are inhibition of __________, increase of _________ _________ from a.a. and fats. Immune response is _________________ and lowered immunity. See ___________________ for long-term effects What target tissue(s) & response for minerlocorticoids? _______________ (ex. _________) target mainly _______________ (_________). The response is an increased re-absorption of _____, (which results in ________________ __________________________) and increased excretion of K+ We will discuss this in more detail while exploring the Excretory (Urinary) system. What Gland? The _______ are _______ sex glands that secrete ___________, which targets many cells in the body and which results in masculinization. The ________ are _______ sex glands that secrete ________ and ______________. These hormones influence female secondary sex characteristics as well as many other functions. We will discuss in more detail during explorations of the Reproductive system. What Gland? The ___________ is in the ____________. It secretes __________, which targets the ________________. The response is decreased ________ secretion. What effect on reproduction? Activity is sensitive to _______.