* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HMC Pulse
Survey
Document related concepts
Bovine somatotropin wikipedia , lookup
Human chorionic gonadotropin wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Vasopressin wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
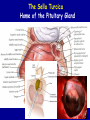
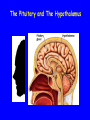
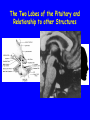
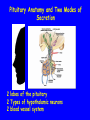
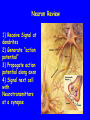
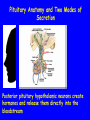
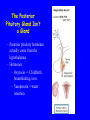
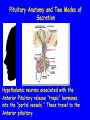
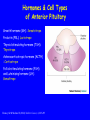
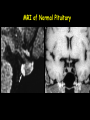
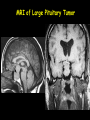
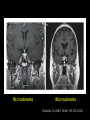
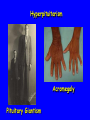
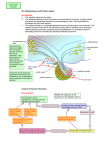
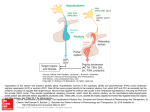
The Sella Turcica Home of the Pituitary Gland What Do the Pituitary and Hypothalamus Do? • Pituitary Gland • Hypothalamus – Secretes/releases hormones – that affect endocrine glands in the body – Regulate other hormones as a – “hormone control center” – Has effects on blood pressure, – growth, metabolism, water retention, body temperature, sexual development, and pregnancy. Receives stimulation/information from various parts of the brain Secretes hormones that regulate the pituitary gland (anterior) Secretes hormones that are released directly by the pituitary (posterior) 2 The Pituitary and The Hypothalamus The Two Lobes of the Pituitary and Relationship to other Structures Pituitary Anatomy and Two Modes of Secretion 2 lobes of the pituitary 2 Types of hypothalamic neurons 2 blood vessel system Neuron Review 1) Receive Signal at dendrites 2) Generate “action potential” 3) Propagate action potential along axon 4) Signal next cell with Neurotransmitters at a synapse Various Brain Cells Regulation of Hypothalamic Secretion by Neurons using “Classical” Neurotransmitters (e.g.serotonin, dopamine) Hypothalamus Cell Pituitary Anatomy and Two Modes of Secretion Posterior pituitary hypothalamic neurons create hormones and release them directly into the bloodstream The Posterior Pituitary Gland Isn’t a Gland – Posterior pituitary hormones actually come from the hypothalamus – Hormones: – Oxytocin -> Childbirth, breastfeeding, love. – Vasopressin ->water retention Pituitary Anatomy and Two Modes of Secretion Hypothalamic neurons associated with the Anterior Pituitary release “tropic” hormones into the “portal vessels.” These travel to the Anterior pituitary. Hypothalamus Releasing Factor (topic hormone) on the Anterior Pituitary – Example – Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH) -> Portal System – Portal System -> Anterior Pituitary – Anterior Pituitary -> Growth Hormone Melmed, S et al (2011) Williams Textbook of Endocrinology, Figure 3-7 Hypothalamic Hormones That Regulate 5 Anterior Pituitary Secretions • Pituitary hormones with positive and negative hypothalamic regulators • Pituitary hormones with positive hypothalamic regulators – Growth hormone controlled by – Thyrotropin releasing hormone • GHRH (+) (TRH)-> Thyrotropin • Somatostatin (-) – Corticotropin releasing – Prolactin controlled by hormone (CRH) • Prolactin inhibitory factor > Corticotropin (PIF; dopamine) (-) – Gonadotropin releasing • Prolactin releasing factor hormone (GnRH) (PRF) (+) -> Gonadotropin Hormones & Cell Types of Anterior Pituitary Growth hormone (GH): Somatotrope Prolactin (PRL): Lactotrope Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH): Thyrotrope Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) : Corticotrope Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing hormone (LH): Gonadtrope Heaney AP & Melmed S (2004) Nat Rev Cancer, 4, 285-295 Homeostasis: Negative Feedback Systems Keep body functions in balance How does this apply to Pituitary hormones? Control of Water Metabolism by Vassopressin (AVP) Hypothalamus Increase in Blood Water Loss viscosity AVP Stimulate Thirst Drink Decreased Blood Viscosity Retain Water Control of Water Metabolism by Vassopressin (AVP) Hypothalamus Increase in Blood Water Loss viscosity AVP Stimulate Thirst Drink Retain Water Decreased Blood Viscosity 16 Thyroid Hormone Feedback System 17 Anterior Pituitary Axes Hypothalamic Control, Hormones and their Targets and Feedback Control Adrenal Axis Thyroid Axis Gonadal Axis Growth HormoneProlactin Axis Axis Melmed, S et al (2011) Williams Textbook of Endocrinology, Figure 8-6 MRI of Normal Pituitary MRI of Large Pituitary Tumor Microadenoma Macroadenoma Schlechte, JA (2003) NEJM, 349, 2035-2041 Effects of Pituitary Adenoma – Visual field defects due to growth pushing on the optic chiasm – Increasing Inter Cranial Pressure – Headaches – Hyperpituitarism – Too much production of one or several hormones Hyperpituitarism Acromegaly Pituitary Giantism Key Points – The Hypothalamus produces hormones that: – Are released by the posterior pituitary – Raise or lower production of anterior pituitary hormones – The pituitary gland: – Produces hormones that regulate other endocrine glands in the body – Each of these hormones has a feedback loop that maintains homeostasis – Disease of the pituitary or hypothalamus can have serious effects