* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to the Body
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
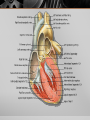
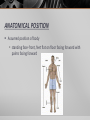
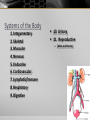
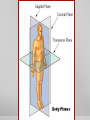
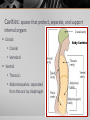
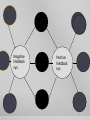
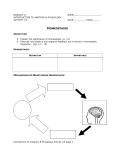
Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy & Physiology Class Mrs. Leisher WHAT IS ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY? Anatomy: study of the structure, shape, and locations of body parts Physiology: study of the function of body parts Principle of Complementarity of Structure & Function - This principle states that function reflects structure Can you think of an example? ANATOMICAL POSITION Assumed position of body standing face-front, feet flat on floor facing forward with palms facing forward Structural level of organization DIRECTIONAL TERMS Superior/inferior Anterior/posterior Medial/lateral Proximal/distal Superficial/deep Systems of the Body 1. Integumentary 2. Skeletal 3. Muscular 4. Nervous 5. Endocrine 6. Cardiovascular 7. Lymphatic/immune 8. Respiratory 9. Digestive 10. Urinary 11. Reproductive (Male and female) Planes: imaginary flat surfaces that pass through the body 1. Sagittal: divides into right and left 2. Frontal: divides into anterior/posterior 3. Transverse: divides into superior/inferior Cavities: spaces that protect, separate, and support internal organs Dorsal: Cranial Vertebral Ventral Thoracic: Abdominopelvic: separated from thoracic by diaphragm IN CLASS ASSIGNMENT: For each system: Write 1-3 sentences that describe the responsibilities of that system. Then list 2-4 organs/components of that system. Work on your sentence NOT being just copied from the book. Sufficient, but concise!!! Illustrate (literal or symbolic) HOMEOSTASIS Maintaining homeostasis is essential for life. Homeostasis: keeping internal conditions relatively stable Maintaining the volume and composition of body fluids important for homeostasis Intracellular Extracellular: EX: blood plasma, cerebrospinal fluid Know examples HOW IS THIS PICTURE A VISUAL REPRESENTATION OF HOMEOSTASIS? Regulated by: The body communicating within itself, constantly regulating the balance in the body. the nervous (fast) or endocrine (slow) system Feedback Systems A cycle of events in which the status of a body condition is monitored, evaluated, changed, remonitored, reevaluated, and so. A disruption that changes a controlled condition (eg temp, blood glucose levels) is called a stimulus Feedback systems cont. 3 components Receptor: structure that monitors changes in a controlled condition and sends input to a control center. EX: nerve endings in finger tips sense temp. change Control center: sets the range of values within which a controlled condition should be maintained, evaluates the input it receives from receptors, and generates output commands when they are needed. EX: the brain or nucleus of cell Effector: structure that receives output from the control center and produces a response that changes the controlled condition. example body temp. drops sharply (stimulus), detected by your hypothalamus (receptor), your brain (control center) sends nerve impulses (output) to your skeletal muscles (effectors). Results in shivering to generate heat to raise your body temp. BIG PICTURE HOMEOSTASIS IS REGULATED BY FEEDBACK SYSTEMS!!!!! _____ disrupts homeostasis Disruption monitored by ___________ which send a message ______ _____: receives message and provides output ______ bring about a change or response that alters the controlled condition Flowchart of a feedback system Negative Feedback Systems Reverses a change in a controlled condition. EX blood pressure returning to normal after increasing. Positive Feedback Systems Strengthens or reinforces a change in one of the body’s controlled conditions EX. Normal childbirth Negative feedback sys. Positive feedback sys. Reverses a change In controlled condition Chemical and electrical messengers Stops as controlled Condition Returns To normal Negative feedback sys. Regulate more common conditions Have receptors Control center effectors Start with stimulus End with response Reinforces a change In a Controlled condition Positive feedback sys. Shut off by outsi event Reinforce events That don’t Happen Very often