* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Characteristics of Life
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
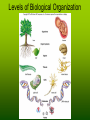
Characteristics of Life • Biology –The study of Life • Bio: Life • ology: Study of Characteristics of Life • Response to Stimulus (Movement) • Growth & Development • Reproduction • Organization • Homeostasis • Use Energy Living things acquire materials and energy, and they reproduce Response to Stimulus • Stimulus is any response to an organism’s environment that causes it to react. Living things grow and develop Growth & Development • All organisms change during their lives • Growth increases size • Development is like the stages of life that humans go through: infant, adolescent, (puberty), adult. Reproduction • The species must reproduce • This is how the species survives • A group of organisms that interbreed and produce fertile offspring are called a species. Reproduction (cont) • Reproduction is a process that can allow gradual change in the characteristics of a species over time. • Change over time is evolution. • Change over time explains the great diversity of life. Organization • Each species has its own type of body organization • Cells, tissues, organs, systems are levels of organization • All body systems interact with other systems. Levels of Biological Organization Homeostasis • The ability of the body of an organism to maintain it’s internal environment or conditions in the body. • Example: Body Temperature • Maintaining balance within the body Use Energy • All living things obtain energy from their environment. • They use this energy to move, grow and develop, reproduce, have organized body systems, and maintain homeostasis. • Autotrophic vs Heterotrophic Theme of Biology • Living things do not exist in isolation • They are all functioning parts in the delicate balance of nature. • Life is dynamic, not static Organization of the Biosphere • Chemical cycling- chemicals cycle through an ecosystem until they are returned to the environment through death and decomposition • Energy cycling-flows from the sun through photosynthesizers to others in food chain and dissipates back to the environment as heat A grassland, a terrestrial ecosystem • Fig 1.6