* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vertebral Column
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
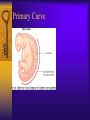
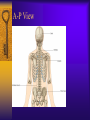
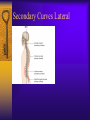
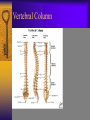
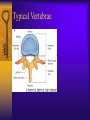
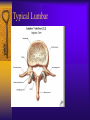
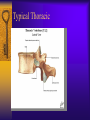
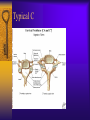
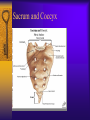
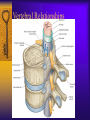
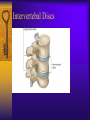
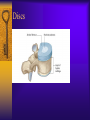
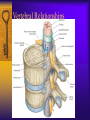
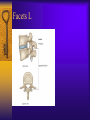
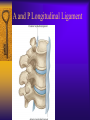
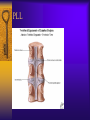
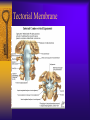
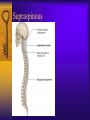
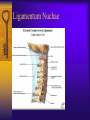
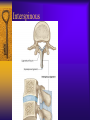
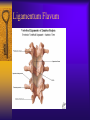
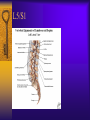
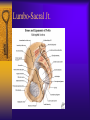
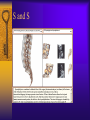
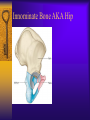
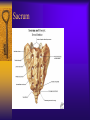
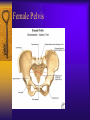
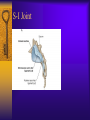
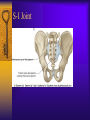
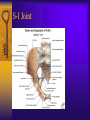
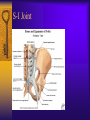
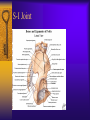
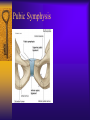
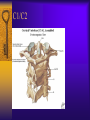
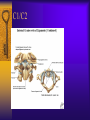
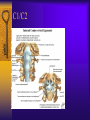
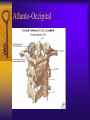
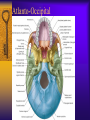
Vertebral Column Osteology 7 C, 12 T, 5 L, 5 S (Fused as Sacrum), 4 coccygeal Primary Curves Secondary Curves Anterior/Posterior alignment Primary Curve Vertebral Segments A-P View Secondary Curves Lateral Vertebral Column Osteology Typical Vertebrae Body – Superior and inferior surfaces of body (plateaus) – Thickened around the rim, location of epiphyseal plates – Cartilaginous end-plates Vertebral Arch – Pedicles, Laminae – Transverse Processes – Spinous Process – Facets – superior articular and inferior articular Spinal Foramen Intervertebral Foramen Typical Vertebrae Typical Vertebrae Typical Lumbar Typical Thoracic Typical C Sacrum and Coccyx Vertebral Relationships Arthrology Intervertebral Discs Fibrocartilaginous joints Increase in size from C to L (3mm to 9 mm) Ratio remains the same Make up 20-30% of length of column Intervertebal Discs Discs Discs Arthrology Two Components Outer rim of fibrocartilage called the anulus fibrosus (attaches to cartilaginous end plate) Connects vertebral bodies in a fibrocartilaginous joint (no capsule, little motion) Arthrology Anulus encloses a central mass called the nucleus pulposus About 80-90% water, less with increased age Contains a mucopolysaccharide matrix Changes shape, releases and absorbs water. Thicker in AM than PM Neither blood vessels or nerves penetrate nucleus Arthrology Structure deforms when pressure is put on vertebral column as in weight bearing Acts as a shock absorber Annulus totally encloses the nucleus and keeps it under constant pressure As you get older, the H2O content decreases and the nucleus becomes more fibrocartilaginous, therefore less easily deformable and more easily damaged Arthrology Nucleus, when under extreme pressure, can herniate or extrude from the disc in a posterior or posterior-lateral direction Usually occurs in cervical or lumbar region Nucleus can put pressure on spinal nerve causing refereed symptoms (motor and sensory) Can cause pressure on cord itself if true posterior Vertebral Relationships Arthrology Facet Joints (Typical) Superior articular facets of one vertebrae with inferior facets of vertebrae above Synovial gliding joints Surrounded by joint capsule and small capsular ligaments The type and amount of motion in any given part of the spine is dictated by the orientation of the articular facets as well as the fluidity, elasticity and thickness of the intervertebral discs Facet Joints (C and T) Facets L Arthrology Typical movements in sections of the spine Lumbar Thoracic Cervical Major Ligaments of the Spine Anterior Longitudinal Ligament Dense band along anterior and lateral surface of the vertebral bodies from C2 to sacrum – Superficial - bridge several vertebrae – Deep – short, run from V to V, blends with fibers of anulus fibrosus – Limits extension of V column From C1 to skull, called Atlanto-Occipital Membrane ALL Atlanto-Occipital Membrane A and P Longitudinal Ligament Major Ligaments Posterior Longitudinal Ligament – Runs along posterior surface of vertebral bodies (anterior to spinal canal) – C2 to Sacrum – Short fibers attach ligament to posterior disc, reinforce disc posteriorly Superiorly, continues to occiput, called Tectorial Membrane Limits flexion PLL Tectorial Membrane Ligaments Supraspinous – Spinous process to spinous process – tip to tip – C7 to sacrum Limits flexion In cervical region, becomes much thicker with a greater elastic content Called Ligamentum Nuchae Supraspinous Ligamentum Nuchae Ligaments Interspinous Found between spinous processes Most well developed in lumbar region support Interspinous Interspinous Ligaments Ligamentum Flavum Connects lamina of one to lamina of the other Found from axis to sacrum Limit flexion Continuation to the skull is called Posterior Atlanto-Occipital membrane Ligamentum Flavum Atlanto-Occipital MembranePosterior Ligaments Intertransverse Only well-developed in Lumbar Region Between transverse processes Limit lateral flexion Special Joints of Spine Lumbo-Sacral – L5 and S1 (or sacrum) – Drastic change from lordotic to kyphotic curve – Strong “shearing forces” – The sacral segment is inclined anteriorly and inferiorly forms an angel with the horizontal called the lumbosacral angle Angle can be increased significantly with an increase in lumbar curve During flexion/extension the greatest mobility of the spine occurs between L5 and S1 L5/S1 Lumbo-Sacral Jt. L5/S1 Spondylolysis – a developmental anomaly of the lamina wherin a bony defect separates the sup. and inf. Articular processes thus separating the post. Part of the neural arch from the ant. Arch and the vertebral body Usually asymptomatic, very common in males S and S L5/S1 Spondylolistheses – an anterior movement of the L5 vertebral body and can cause compression of the cauda equina which rests posteriorly Sacralization Where 5th lumbar vertebrae takes on characteristics of the sacrum and may be partially or completely fused with sacrum Lumbarization Superior aspect of the sacrum assumes characteristics of the 5th lumbar vertebrae S-I Joint Review Hip Bone AKA Innominate AKA Os Coxae Ilium, Ischium and Pubis Fuse at Puberty Acetabulum Pelvis = 2 coxal bones the sacrum and coccyx Innominate Bone AKA Hip Sacrum Pelvis Female Pelvis S-I Auricular surface of ilium with auricular surface of sacrum-Little movement Joint under relatively constant pressure to rotate anteriorly based on anatomical design Upper part of joint is not synovial, is fibrous held in place by tough Interrosseous S-I ligaments – helps limit anterior motion S-I Joint S-I Joint S-I Joint S-I – Synovial Aspect of Joint Major Ligaments – mostly designed to prevent ant. motion Posterior S-I – runs down and medially from ilium to sacrum Iliolumbar – L4 and 5 transverse processes to posterior iliac crest Anterior S-I – ilium to sacrum Sacrotuberous – iliac tuberosity and post. Surface of lower sacrum to ischial tuberosity Sacrospinous – lateral borders of lower sacrum and coccyx to attach to the spine of ischium S-I Joint S-I Joint Pubic Symphysis Anterior connection of pelvis Fibrocartilaginous joint Limited motion Motion increase dramatically during pregnancy, especially at the time of birth Similar increase in SI joint mobility at this time Pubic Symphysis Atlanto-Axial Joint Atlas and Axis Pivot Two convex superior facets of axis with two concave inferior facets of the atlas Atlas also posses a facet on the internal surface of the anterior arch which articulates with the dens of the axis Major ligaments form spine support – Ant. Atlanto-Occipital, Tectorial Membrane, Post. A-O C1/C2 C1/C2 C1/C2 A-A Joint Alar – from dens to occiput Transverse - around dens Cruciate – Sup. Longitudinal Band – Inferior Longitudinal Band – Transverse Atlanto-Occipital Joint Two concave superior facets of atlas articulate with two convex surfaces of occipital condyles of the skull Supported by major ligaments Small saddle joint Very limited motion – nodding type motions in all directions. Atlanto-Occipital Atlanto-Occipital