* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Skeletal System Notes Day 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
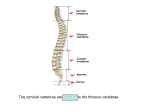
Anatomy Notes Day 3: The vertebral Column Name: The Spine: 1) The______________________________, extends from the skull, which it supports, to the pelvis, where it transmits the weight of the body to the lower limbs. 2) 2. Of the 24 single bones: 1. 2. 3. 3. The single vertebrae are separated by pads of fibrocartilage known as the ____________________________which cushion the vertebrae of and absorb shocks while providing the spine with flexibility. 4. The discs and the __________________________structure of the vertebral column work together to prevent shock to the head when we walk or run. 5. The spinal curvatures in the thoracic and sacral regions are called the _________________________because they are present when we are born. 6. Later, the ______________________________develop. Homeostatic Imbalance: 1. There are several types of abnormal spinal curvatures: a. b. c. Vertebra Structure: 1.______________________: is the disc-like, weight bearing part of the vertebra facing anteriorly in the vertebral column. 2.___________________: the arch formed from the joining of all posterior extensions, the laminae and pedicles, from the vertebral body. 3._____________________: the canal through which the spinal cord passes. 4. ___________________________ two lateral projections from the vertebral arch. 5. __________________________single projection arising from the posterior aspect of the vertebral arch. 6._________________________________________paired projections lateral to the vertebral foramen, allowing a vertebra to form joints with adjacent vertebrae. Cervical Vertebra: 1. The __________________has no body. The superior surfaces of its transverse processes contain large depressions that receive the occipital condyles of the skull. This joint allows you to nod “yes”. 2. _____________________acts as a pivot for the rotation of the atlas (and skull). 3. It has a large, upright process, ___________________________________which acts as a pivot point. 4. The _____________________________₂ allows you to rotate your head from side to side to indicate “no”. 5. The “typical” cervical vertebrae are ___________________and are the smallest, lightest, vertebrae, and most often their ___________________ are short and divided into two branches. 6. The ___________________________of the cervical vertebrae contain foramina (openings) through which the vertebral arteries pass on their way to the brain above. Thoracic Vertebrae: 1. The _____________________________are all typical. 2. They are larger than the cervical vertebrae, and the body is somewhat heart-shaped and has two __________________________________________on each side, which receive the heads of the ribs. 3. The __________________________is long and hooks sharply downward, causing the vertebra to look like a giraffe’s head viewed from the side. Lumbar Vertebrae: 1. The __________________________________________have massive, block-like bodies, and have short, hatchetshaped spinous processes that make them look like a moose head from the side. Sacrum: 1. The _____________________is formed by the fusion of five vertebrae. 2. The wing-like _________________articulate laterally with the hip bone, forming the sacroiliac joints. 3. Its posterior midline surface is roughened by the__________________________________, the fused process of the sacral vertebrae. 4. The vertebral canal continues inside the sacrum as the sacral canal and terminates in a large inferior opening called the _______________________________. Coccyx: 1. The ___________________is formed from the fusion of three to five tiny, irregularly shaped vertebrae. Label the following diagram with the correct vertebrae (Cervical, thoracic, etc.)