* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomy and Physiology Name: Chapter 6 DRO Period: The Human
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
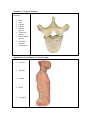
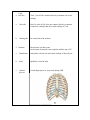
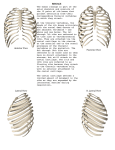
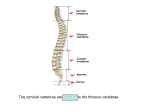
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO The Human Vertebral Column Name: Period: General Vertebrae Characteristics: *each vertebrae has two essential parts: the body and the arch 1. Two Essential parts of each vertebra: a. The Centrum b. The Arch: i. The arch is composed of: Processes of the pedicle and laminae: *the body – largest part of vertebrae *the arch is composed of the pedicle(2) and the lamina(2) *pedicle: two short pieces of thick bone *lamina: two broad plates of bone that enclose the spinal foramen 1. spinous process(1) *projects back from laminae *site for muscle attachement *acts as a lever to move structures 2. articular process (4) *2 superior and 2 inferior *forms a joint with the inferior or Superior process of adjacent vertbrae *arise where the pedicle and lamina meet 3. transverse process (2) *where the pedicle joins the body *attachment site for muscles *acts as a lever to move a structure Other structures: *vertebral foramen – where spinal cord passes * costal facets- where ribs articulate with vertebrae (thoracic Anatomy of a Typical Vertebrae: Label the following structures: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Body Arch Lamina Pedicle Spinous process Transverse process Sup. Articular process Vertebral foramen Costal facets Organization of the Human Vertebral Column: 1. Cervical 2. Thoracic 3. Lumbar 4. Sacral 5. Coccygeal Typical Vertebrae of the Human Vertebral Column: Label all structures on the following vertebra 1. Atlas *First cervical vertebrae *articulates with the occipital condyle of the skull *allows for up and down nodding motions 2. Axis *Second cervical vertebrae *allows for left to right motion of the skull 3. Typical Cervical Vertebrae: *top of the spinal column *forms flexible framework of the neck *supports head *7 4. Typical Thoracic Vertebrae: *larger than cervical vertebrae *articulates with the ribs (costal facets) *increases in size from top to bottom *supports upper body weight *large spinous process projecting downward and back *12 5. Typical Lumbar Vertebrae: *has a very large body, to support most of the weight of the upper body *least mobile- limited mobility *subjected to pressure and stress- easily herniated *has lateral processes which are rudimentary ribs- called costal processes *massive spinous process for attachment of large back muscles *cauda equine- at the L4 location, the spinal chord flares out into a bundle of nerves that resembles a horse tail *5 6. Sacrum: *5 bones fused into a single bony plate *forms sacroiliac joint with the ileum of the hip- transmits weight from the upper body to the pelvic girdle and lower extremities *ventral surface is concave *dorsal surface is convex *tail bone- fusion of 3-5 bones in humans 7. Coccyx 8. Thoracic Cage: a. true ribs * first 7 pair of ribs- connects directly to sternum via costal cartilage a. false ribs *last five pairs of ribs- does not connect directly to sternum *connects to cartilage that fuses with cartilage of 7 rib b. floating ribs *no connection with sternum 9. Sternum *breast bone- has three parts *oscification of sternum is not complete until the age of 25 a. Manubrium *articulates with clavicle and costal cartilage of first rib pair b. body *gladiolus- sward in latin c. xiphoid process *sward shaped process- may break during CPR