* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Thoracic Cage
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
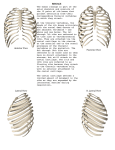
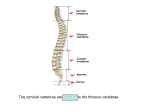
The Thoracic Cage • It is also known as the chest cavity or thorax - It is the skeleton of the chest • It consists of 3 parts: a) dorsal aspect – thoracic vertebrae b) lateral aspect – ribs c) anterior aspect – sternum and cost cartilages • Functions: a) protects the heart and lungs b) provides support to the pectoral girdle and upper limbs c) attachment point for many muscles of the chest, back and shoulders d) helps in breathing – intercostal spaces lift to inhale and depress to exhale Parts of the Thoracic Cage Sternum – consists of 3 bones fused together manubrium, body, xiphoid process parts of the thoracic cage continued… Manubrium • superior and widest portion of the bone • Clavicular notch – point where the clavicles articulate with the sternum • • • Body of the sternum Largest portion of the sternum Costal cartilages articulate from the ribs to attach to the body Sternal angle – 2nd rib articulates where the body meets the manubrium Xiphoid process • Smallest and inferior portion of the bone • Attachment of important muscles – diaphragm and rectus abdominis Ribs True Ribs • First 7 pairs connect directly to the sternum by the costal cartilages False Ribs • Ribs 8 to 11 do not attach directly to the sternum – attach by costal cartilages Ribs continued… Floating Ribs • Ribs 11 and 12 with no connection to the sternum however they attach to the vertebrae in the dorsal aspect NOTE: • Spaces between the ribs are known as intercostal spaces – blood vessels, nerves, and intercostal muscles occupy these spaces • These muscles contract and permit expansion of the thoracic cavity during inhalation then relax and permit depression during exhalation Hyoid Bone • Located in the neck tissue and does not articulate with any other bone • Articulates with the pharyngeal and neck muscles The Vertebral Column • • • • • • Also known as the spinal column It consists of 26 bones It is strong, flexible series of bones that bends in the anterior, posterior, and lateral aspects it encloses and protects the spinal cord Supports the head and it is an attachment point for the ribs and muscles of the back Openings between the vertebrae are known as intervertebral foramina – which allows nerves to pass from the spinal cord to other parts of the body 5 divisions of the Vertebral Column: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Cervical - 7 vertebrae; neck region Thoracic – 12 vertebrae; chest region Lumbar – 5 vertebrae; lower back Sacral – 1 vertebra - the sacrum (group of 5 vertebrae fused as one large bone) Coccygeal – 1 vertebra – the coccyx (group of 3-5 fused vertebrae) Vertebral column continued… Parts of the Vertebra Body/Centrum • Anterior end of the bone – cylindrical in shape • Superior and inferior surfaces where the body articulates with intervertebral discs • Small veins and arteries pass through the body Vertebral Arch • Formed by a floor – posterior aspect of the body • Its walls are called pedicles Laminae • Roof of the vertebral arch Vertebral Foramen • Opening of the neural arch where the spinal cord passes along with connective tissue and blood vessels Parts of the vertebrae continued… Spinal Process • Projects posteriorly and inferiorly from the laminae • Also known as the spine of the vertebrae • Attachment point for muscles Transverse Process • Where the lamina and pedicle join • Extends laterally to each side of the vertebra • Attachment point for muscles Superior Articular Process • Forms the joint with other vertebrae • The surface of this process is called a facet