* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Vertebral Column
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
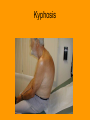
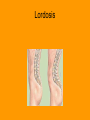
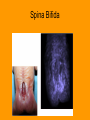
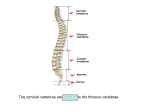
The Vertebral Column General Characteristics • • • • Formed from 26 irregular bones Axial support of trunk Surrounds and protects spinal chord Provides attachment points for ribs and muscles of back Divisions and Curvatures • 70 cm (28 in) long • 5 divisions: 7 vertebrae are cervical, the next 12 are thoracic, and the 5 supporting the lower back are lumbar, the sacrum is inferior to the lumbar, and the coccyx or tail bone • Has an S or springlike shape Cervical Vertebrae • Identified as the first 7 vertebrae c1 to c7 • Smallest and lightest • Typical features of c3 to c7 vertebrae – Body is oval – The spinous is short, projects directly back and is bifid (split at its tip) except c7 – The vertebral foramen is large and generally triangular – Each transverse process contains a transverse foramen through which the vertebral blood vessels pass to brain – C7 is larger than other cervical vertebrae, spinous process is visible through skin and is used to count (called vertebra prominens) Cervical Vertebrae Continued • C1 and c2 vertebrae (the atlas and axis) have no intervertebral disc between them • C1 the atlas, has no body and no spinous process, it is a ring of bone consisting of anterior and posterior arches and a lateral mass on each side. It carries the skull and the superior articular facets receive the occipital condyles allowing you to nod • C2 the axis, has a body, spine, and other typical vertebral processes. Has a knoblike dens (odontoid process) projecting superiorly from body. Forms a joint that allows you to shake head no Thoracic Vertebrae • 12 vertebrae (T1 to T12) all articulate with ribs • Increase in size from first to last • Characteristics – Roughly heart shaped, have two facets on each side that receive the head of ribs – Have a circular vertebral foramen – The spinous process is long and points sharply inferiorly – Except T11 & T12, the transverse processes have facets that articulate with the tubercles of ribs Lumbar Vertebrae • • • • Commonly called small of back, receives most stress 5 vertebrae (L1 to L5) Massive bodies and kidney shaped Characteristics – The pedicles and laminae are shorter and thicker than other vertebrae – The spinous processes are short, flat, and hatchet shaped and are easily seen when a person bends. Processes project backward for attachment of back muscles – The vertebral foramen is triangular – The orientation of the facets of the articular processes of the lumbar vertebra lock the vertebrae together and keeps the rotation of the lumbar spine Sacrum • • • • • Roughly heart shaped Formed by 5 fused vertebrae Strengthens and stabilizes the pelvis Forms the sacroiliac joint with hip bones The sacral promontory, the anterosuperior margin of the first sacral vertebra, bulges into pelvic cavity. It is used as a landmark for obstetricians and the body’s center of gravity lies about 1 cm posterior to it Coccyx • The tail bone “cuckoo” because looks like birds beak • Small triangular bone, consisting of four vertebrae fused together • Articulates superiorly to the sacrum • Useless bone, only provides slight support to pelvic organs Disease of Vertebrae • Scoliosis: “twisted disease” – An abnormal lateral curvature of spine – Common late childhood, especially in girls – Result from abnormal vertebral structure, lower limbs of unequal length, or muscle paralysis – Severe cases must be treated with braces or surgery before growth ends to prevent permanent deformity and breathing difficulties Vertebrae Disease Continued • Kyphosis – – – – “hunchback” A dorsally exaggerated thoracic curvature Common in elderly due to osteoporosis May also be due to to tuberculosis of spine, rickets, or osteomalacia • Lordosis – – – – “Swayback” Accentuated lumbar curvature Caused by spinal tuberculosis or rickets May be temporary: “beer guts” in men, pregnancy in women • Prolapsed disc – Herniated disc caused by trauma to back Kyphosis Lordosis Prolapsed Disk Vertebrae Disease continued • Spina Bifida – “Cleft Spine” – Congenital defect of the vertebral column in which the vertebral laminae fail to fuse medially – May result in impairment of neural functioning and may cause nervous system infections Spina Bifida