* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomical position
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
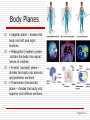
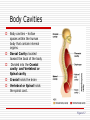
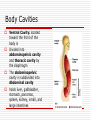
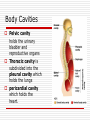
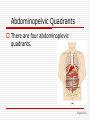
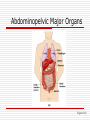
Language of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Special terminology is used to prevent misunderstanding Exact terms are used for: Position Direction Regions Structures Anatomical Position Anatomical position is a standardized method of observing or imaging the body that allows precise and consistent anatomical references. When in the anatomical position, the subject stands: standing upright facing the observer, head level eyes facing forward feet flat on the floor arms at the sides palms turned forward (ventral) Orientation and Directional Terms Superior- Towards the head end or upper part of the body. ABOVE Inferior- Away from the head end or toward the lower part of the structure. BELOW Anterior- Toward or at the front of the body. IN FRONT OF Posterior- Toward the or at he backside of the body. BEHIND Table 1.1 Orientation and Directional Terms Medial- Toward or at the midline of the body. ON THE INNER SIDE OF Lateral- Away from the midline of the body. ON THE OUTTER SIDE OF Intermediate-Between a more medial and more lateral structure Proximal- Close to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body truck. Orientation and Directional Terms Distal- Farther from the origin of the body part or point of attachment of a limb to the body truck Superficial- Toward or at the body surface Deep- Away from the body surface; more internal Body Landmarks Anterior Figure 1.5a Body Landmarks Posterior Figure 1.5b Body Planes • Sagittal plane – divides the body into left and right sections. • Midsagittal (median) planedivides the body into equal halves at midline. • Frontal (coronal) plane divides the body into anterior and posterior sections • Transverse (horizontal) plane – divides the body into superior and inferior sections. Figure 1.6 Body Cavities Body cavities – hollow spaces within the human body that contain internal organs. Dorsal Cavity: located toward the back of the body Divided into the Cranial cavity and Vertebral or Spinal cavity Cranial holds the brain Vertebral or Spinal holds the spinal cord. Figure 1.7 Body Cavities Ventral Cavity: located toward the front of the body is Divided into abdominopelvic cavity and thoracic cavity by the diaphragm The abdominopelvic cavity is subdivided into Abdominal cavity holds liver, gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, spleen, kidney, small, and large intestines Body Cavities Pelvic cavity holds the urinary bladder and reproductive organs Thoracic cavity is subdivided into the pleural cavity which holds the lungs pericardial cavity which holds the heart. Abdominopelvic Quadrants There are four abdominoplevic quadrants. Figure 1.8a Abdominopelvic Regions The abdominal area is subdivided into 9 regions. Figure 1.8b Abdominopelvic Major Organs Figure 1.8c