* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
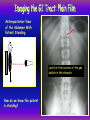
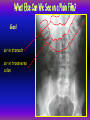
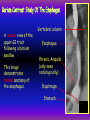
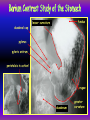
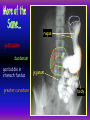
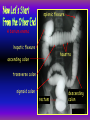
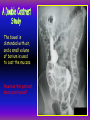
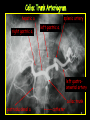
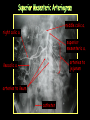
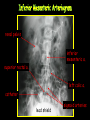
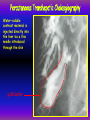
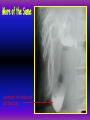
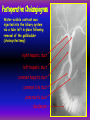
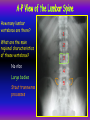
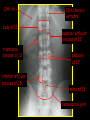
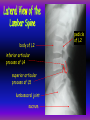
Anteroposterior View of the Abdomen With Patient Standing Look for the location of the gas bubble in the stomach How do we know the patient is standing? Air bubble in fundus of stomach Liver outline Vertebrae T12 L1 Gas! air in stomach air in transverse colon A lateral view of the upper GI tract following a barium swallow This image demonstrates normal anatomy of the esophagus Vertebral column Esophagus Phrenic Ampulla (only seen radiologically) Diaphragm Stomach duodenal cap fundus lesser curvature pylorus pyloric antrum peristalsis in action! rugae duodenum greater curvature rugae gallbladder duodenum gas bubble in stomach fundus greater curvature jejunum body splenic flexure A barium enema hepatic flexure haustra ascending colon transverse colon sigmoid colon rectum descending colon The bowel is distended with air, and a small volume of barium is used to coat the mucosa How has the patient been positioned? hepatic a. right gastric a. splenic artery left gastric a. left gastroomental artery celiac trunk gastroduodenal a. catheter middle colic a. right colic a. superior mesenteric a. arteries to jejunum ileocolic a. arteries to ileum catheter renal pelvis inferior mesenteric a. superior rectal a. left colic a. catheter lead shield sigmoid arteries Water-soluble contrast material is injected directly into the liver via a fine needle introduced through the skin gallbladder contrast in fundus of gallbladder Water-soluble contrast was injected into the biliary system via a tube left in place following removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) right hepatic duct left hepatic duct common hepatic duct common bile duct pancreatic duct duodenum How many lumbar vertebrae are there? What are the main regional characteristics of these vertebrae? No ribs Large bodies Stout transverse processes 1 2 3 4 5 12th rib body of L1 transverse process of L2 inferior articular process of L4 12th thoracic vertebra superior articular process of L2 pedicles of L3 spine of L5 lumbosacral joint body of L2 inferior articular process of L4 superior articular process of L5 lumbosacral joint sacrum pedicle of L2