* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Back - chancescience
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
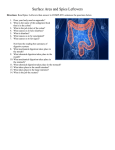
This is Jeopardy Digestive System 1 Category Category Category Category Category No. 1 No. 2 No. 3 No. 4 No. 5 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Final Jeopardy 2 C1-100-The answer is… Which organ is responsible for dehydration and compaction of indigestible materials? Large intestine Back 3 C1-200-The answer is… The lateral walls of the oral cavity are formed by the cheeks Back 4 C1-300-The answer is… Peyer’s patches are found in the_____. What is their function? Small intestine, part of the immune system – kills pathogens Back 5 C1-400-The answer is… How many total sections make up the L.I.? Name them. 6 – cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum Back 6 C1-500-The answer is… This portion of the stomach attaches to the esophagus through this sphincter. Cardia, cardioesophageal sphincter Back 7 C2-100-The answer is… The muscular tube of the digestive system can also be referred to as the: (2 answers) GI tract or alimentary canal Back 8 C2-200-The answer is… Name the 3 salivary glands Parotid, sublingual, submandibular Back 9 C2-300-The answer is… In which part of the S.I. is the plicae and villi most developed? jejunum Back 10 C2-400-The answer is… Which part of the S.I. attaches to the pylorus of the stomach? duodenum Back 11 C2-500-The answer is… What do parietal cells secrete? HCl Back 12 C3-100-The answer is… Waves that propel material along the G.I. are called: peristalsis Back 13 C3-200-The answer is… What connects the tongue to the underlying epithelium? Lingual frenulum Back 14 C3-300-The answer is… Which part of the S.I. attaches to the L.I.? ileum Back 15 C3-400-The answer is… Name the duct that connects the liver to the duodenum. Hepatic duct to the common bile duct Back 16 C3-500-The answer is… What is the name of the enzyme that breaks down lipids? From where is it released? Lipase, from the pancreas Back 17 C4-100-The answer is… What are haustra? External pouches on the L.I. Back 18 C4-200-The answer is… This is a sheet that hangs like an apron over the abdominal viscera. Greater omentum Back 19 C4-300-The answer is… There are four sections of the stomach. Name them. Cardia, fundus, body, pylorus Back 20 C4-400-The answer is… What is the approximate pH of the mouth? Of the stomach? 7.0, 1.5-2.0 Back 21 C4-500-The answer is… These are the prominent ridges in the stomach. rugae Back 22 C5-100-The answer is… What organ secretes bile and where is it stored? Liver and gallbladder Back 23 C5-200-The answer is… This type of cell secretes mucus. Goblet cells Back 24 C5-300-The answer is… What is the saclike structure that joins the ileum to the L.I. at the ileocecal valve? cecum Back 25 C5-400-The answer is… These type of cells secrete pepsinogen Chief cells Back 26 C5-500-The answer is… This is the space between the lips or cheeks and the teeth. vestibule Back 27 Final Jeopardy 1.List the main organs of the GI tract and the function of each. 2. List 4 accessory organs and their function. 1. mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, S.I., L.I. 2. Pancreas, liver, gallbladder, teeth, tongue, salivary glands Back End Game 28 Mouth – mechanical digestion, chemical digestion of carbs Pharynx – passage of bolus – protection of trachea by epiglottis Esophagus – passage of bolus to stomach – peristalsis Stomach – mechanical mixing of chyme, chemical digestion of protein, continued chemical digestion of carbs. S.I. – breakdown of lipids and remaining nutrients, absorption of nutrients into bloodstream L.I. – reabsorption of water, release of vitamins by bacteria, storage of fecal matter Pancreas – release of buffers, enzymes (lipase, protease, intestinal amylase), regulation of blood sugar levels via insulin Liver – over 400 functions, metabolic regulation, hematologic regulation, production of bile Gallbladder – storage of bile Teeth/tongue – mechanical digestion of food Salivary glands – moisten mouth, flush bacteria, release of 29 amylase