* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Abdominal Viscera
Liver support systems wikipedia , lookup
Bariatric surgery wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hepatocellular carcinoma wikipedia , lookup
Wilson's disease wikipedia , lookup
Colonoscopy wikipedia , lookup
Cholangiocarcinoma wikipedia , lookup
Liver transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Intestine transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Liver cancer wikipedia , lookup
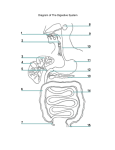
Notes on Digestive System Digestive tract is a “tube” (esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine) with outgrowths (liver, gallbladder, pancreas, vermiform appendix). ESOPHAGUS The esophagus ends in the abdomen and is continuous with the cardia of the stomach. STOMACH Cardia: portion about the esophagus entrance Fundus: the ballooning portion superiorly Body: main part of stomach Pylorus: terminal portion with thickened walls and sphincter opening into the duodenum of the small intestine. The sides of the stomach are the greater and lesser curvature. Fed by gastric artery (branch from celiac artery) SMALL INTESTINE main function is absorption of nutrients Fed by superior mesenteric artery Duodenum “12 fingers” first part of small intestine where most of digestion occur retroperitoneal (outside of abdominal cavity), with exception to first part “C” shaped hepatopancreatic ampullae – where pancreatic duct and bile duct come together main pancreatic duct – buffers and enzymes from pancreas common bile duct – receives bile from gall bladder Jejunum and ileum peritoneal (within abdominal cavity) jejunum is about 2/5 the total length of the rest of the small intestine ileum is the other 3/5 ileocecal valve: the junction between ileum and large intestine controls passage of intestinal contents heard as a loud gurgling sound LARGE INTESTINE fed by inferior mesenteric artery main function is compaction of chime making it feces taniae coli - longitudinal smooth muscle bands - create haustra during contraction - contain appendices epiploicae - fatty appendages large intestine begins at the cecum cecum continues in absorbing nutrients from chyme cecum continues into the ascending colon ascending colon: becomes retroperitoneal as it ascends ascends up the right side of the abdominal cavity turns at the right colic flexure and becomes the transverse colon Transverse colon: becomes peritoneal transverses inferiorly to the greater curvature of the stomach turns at the left colic flexure, and becomes the descending colon Descending colon: becomes retroperitoneal descends down the left side of the abdominal cavity When it becomes peritoneal, it is called the sigmoid colon Sigmoid colon: terminates as the rectum lying directly on the sacrum LIVER gland nutrient processing center and detoxification center peritoneal fed by common hepatic artery porta hepatica (root of liver): location of the hepatic ducts (where bile is sent to the duodenum), hepatic portal vein and hepatic arteries hepatic portal vein – brings blood from digestive tract to liver for detoxification hepatic arteries – blood from descending aorta to liver common hepatic duct brings bile from the liver to duodenum (connects with the cystic duct of the gallbladder) Hepatic veins (not part of root of liver) drains directly into the IVC from liver GALLBLADDER Stores and concentrates bile made in the liver stimulated to contract after a meal peritoneal Cystic duct: brings bile from the gallbladder to the common hepatic duct now called common bile duct (cystic duct and common hepatic duct) empties into the duodenum PANCREAS secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum via pancreatic duct pancreatic duct joined by common bile duct at the hepatopancreatic ampulla retroperitoneal sits in the curvature of the duodenum SPLEEN NOT part of digestive system Largest Lymphoid organ Peritoneal (within body cavity) Fed by splenic artery