* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fetal Pig Structure Function Practice
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
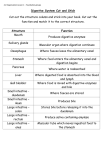
Fetal Pig Structures & Functions Practice Caecum (or cecum) Diaphragm Gallbladder Liver Pancreatic Duct Rugae Stomach Common Bile Duct Duodenum Jejunum Mesentery Pyloric Valve (Sphincter) Small Intestine Villi (in sm. Intestine) Cystic Duct Esophagus Large Intestine Pancreas Rectum Spleen o blind projection located at the junction of the ileum and colon that serves as a sac where fermentation of cellulose occurs. o canal through which digestive enzymes produced by the pancreas are transported to the duodenum. o connective membrane that suspends body organs in the abdominal cavity and holds them together. o distal end of the intestinal tract; primary function is to reabsorb water and produce dry, concentrated feces. o ductless, vascular organ in the abdominal cavity that is a component of the circulatory system; stores blood, recycles worn-out red blood cells and produces lymphocytes. o finger-like projections that increase the surface area of the small intestine and increase absorption of vitamins o first portion of the small intestine; function primarily in final stages of chemical digestion and begins the process of nutrient absorption. o granular organ located along the left margin of the duodenum and the caudal margin of the stomach; produces digestive enzymes and a variety of hormones. o large U-shaped digestive reservoir for food. Chemicals are secreted by its walls which break down the food into microscopic particles that may be absorbed by the cells of the intestines. o large, multi-lobed organ of the abdominal cavity located just caudal to the diaphragm; secretes bile, filters toxins and nutrients from the blood and stores sugars. o larger tubular structure that receives the liquid waste products of digestion, reabsorbs water and minerals, and forms and stores feces for defecation. o middle portion of the small intestine extending from the duodenum to the ileum; primarily responsible for nutrient absorption. o muscular passageway connecting the mouth and oral cavity to the stomach. o muscular sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities; used to ventilate the lungs of mammals. o organ located on the underside of the liver which stores bile and releases it into the duodenum. o regulates the flow of food from the stomach to the small intestine o responsible for most chemical digestion and absorption of nutrients o ridges and folds of the inner wall of the stomach which increase the surface area of the stomach lining and provide texture for the manipulation of food as it is broken down. o tubule that transports bile from the gallbladder into the common bile duct. o tubule through which bile is transported from the liver to the gallbladder and from the gallbladder to the duodenum.