* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Advertising wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Targeted advertising wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Advertising management wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
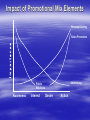
Chapter Thirteen Ford Thunderbird Ad Integrated Marketing Communications Chapter Objectives Discuss the concept and stages of Integrated Marketing Communication. Identify various marketing communication elements and the importance of AIDA. Discuss factors that impact the relative mix of communication elements in an Integrated Marketing Communication plan. Explain methods for measuring the effectiveness of marketing communication. Integrated Marketing Communications Integrated Marketing Communications: – The coordination and integration of all marketing communication tools, avenues, and sources within a company into a seamless program designed to maximize the communication impact on consumers, businesses, and other organization constituencies. Promotion: – All forms of external communications directed toward consumers and businesses with an ultimate goal of developing customers. Reasons for Integrated Marketing Communication – Customers are better informed. – Customers are more price conscious. – Customers are more demanding of quality and service. – Customers want more convenience and faster delivery. Communication to four primary groups: – Customers – Channel members – Employees – Stakeholders Communication Venues • • • • Advertising Sales/Trade promotion Personal selling Public relations • Internet • Database • Direct marketing Traditional Approach radio, television, newspaper, and magazines Integrated Approach Internet, billboards, transit signs, and company stationery Advertising: Paid communication directed to customers and/or other stakeholders Public relations: Addresses issues faced by an organization and represents the organization to the public, media, and various stakeholders Publicity: An outcome of public relations that is produced by the news media and is not paid for or sponsored by the business Sales promotions: Incentives used to encourage end-users to purchase a product, e.g., coupons, premiums Trade promotions: Incentives directed toward channel members to encourage them to purchase, stock or push a product through the channel Personal selling: Direct communication between the buyer and seller with the express purpose of selling a product Database marketing: Collection, analysis, and use of large volumes of customer data to develop marketing programs and customer profiles Direct marketing: Promotion of a product directly from the manufacturer or producer to the buyer without any middlemen involved in the transaction Internet marketing: Promotion and sale of products through the Internet (more than 60% of Americans have Internet access) The Communication Mix Sales Promotions 25% Advertising 25% Trade Promotions 50% Stages of Integrated Marketing Communications 1. Identifying, coordinating, and managing all forms of external communication to bring all of the company’s brands and divisions under central control. Use same logos, themes, and colors (same message, same look). 2. Extending the scope of communication to include everyone touched by the organization. Internal and External communication have to be consistent. Every person who comes in contact with the organization should see one overall theme. 3. Databases are developed to include every customer's activities, purchases, and interactions with the company. Customers information is used to make product and promotion decisions. 4. Establish “a customer value” for each customer. Customers are very different, e.g., some buy large quantities others not, some are loyal others are not. Use individualized marketing approaches that will maximize the return of effort. The Communication Process Noise: different accessibility of medium, selective awareness, attention, reaction, action. Sender Recipient Purpose*: Persuasive Communication It is difficult to guarantee that the intended message of the sender is the perceived message of the recipient. AIDA – model Attention: Get awareness of your message. Interest: Get consumer to listen to message. Desire: Get consumer to want product + service + idea. Action: Get Consumer to purchase. Aida Concept AIDA Concept Attention Interest Retail sales situation A store sign offering $25 off catches your attention. A sign by the exercise bike highlights the low cost and features of the bike. Desire You sit on the bicycle and it feels more comfortable than any others you have tried. Action When a salesperson tells you that it can be purchased now and, if, for any reason, you don’t like the bike, you can bring it back within 30 days for a full refund, you decide to purchase it. Television advertisement A well-built young man appears on the screen wearing only shorts. You have been wanting an exercise bike and this is a model you have not seen before so you want to see what it looks like and what features it has. After seeing the TV ad, you check the Internet to see where the closest retail store is located and what the website says about the bike. Having thought about the exercise bike, you see another advertisement. You decide this is the right bike and make a decision to purchase it, using the tollfree number listed on the TV screen. Model of Communications “*Copy” Encoding Source Message *Informer *Presentation Noise Audience Medium Decoding *Receivers Low Involvement Cognitive Behavioral Affective *Responses *Vehicle High Involvement Cognitive Affective Behavioral Communication Objectives Increase demand – Use trade promotions (channel) – Use sales promotions (consumers) – Advertising and personal selling support Differentiate a product – Avoid commodity status, price competition – Benefits and product attributes – Psychological superiority – Personal selling – Advertising Reduce purchase risk – – – – New products New customers Personal selling Trade and sales promotions Provide information – Advertising – Personal selling • Retail • Field sales Build brand equity – Essential for long-term survival – Two foundations • Quality • Awareness – Advertising Stimulate trial – Sales promotions – Advertising – Personal selling Communication Objectives Summary Objective Promotion Personal Advertising Trade Sales Selling Increase demand M E E G Differentiate a product E P M E Provide information E P P E Build brand equity E P P M Reduce purchase risk P G G E Stimulate Trial M P E M E = Excellent, G = Good, M = Moderate, P = Poor Impact of Promotional Mix Elements Personal Selling Sales Promotion Advertising Public Relations Awareness Interest Desire Action Trustworthy Sources of Information Word-of-Mouth: Whether on-line or off-line, nationally or internationally, friends and family or strangers, word-of-mouth information is typically deemed more trustworthy than information generated by a marketer. This is one reason why marketers are currently exploring “social networks” as a means of message delivery. Business versus Consumer Marketing Business Marketing: Relies more on personal selling and trade promotions (larger volume purchases) Consumer Marketing: Relies more on sales promotion and advertising % of Total Marketing Budget 60.0% 52.6% 50.0% 40.0% 30.1% 30.0% 20.0% 22.6% 19.6% 21.2% 11.3% 10.0% 11.9% 8.8% 4.1% 5.2% 5.3% Radio Magazine 7.2% 0.0% Television Newspaper Telephone Marketing Marketing Methodology/Media Business-to-Business Consumer Direct Mail Push/Pull Marketing Strategies Push marketing strategy: The manufacturer attempts to push the product through the channels with the belief that if the product is available in retail outlets, consumers will purchase it. Pull marketing strategy: The manufacturer builds product demand at the consumer level with the belief that consumers will go to retailers and demand that the product be stocked. Push Strategy < ------------------------------------------------------------ > Pull Strategy Low < ---------------------Advertising ------------------------------- > High High < ------------------------- Trade Promotions -------------------------------- > Low Low < -----------------------Sales Promotions -------------------------------- > High High < ------------------------- Personal Selling -------------------------------- > Low Question: Does Tree Top use a push or a pull strategy? Answer: It uses a pull strategy, advertising their juice to parents, who then demand the product from retailers. Source: © Tree Top, Inc., 2002. Created by Cole & Weber / Red Cell, Seattle, WA. Marketing Communication & the PLC Introduction Advertising – – – Encourage trial usage *** – Good for b-to-b market *** Poor for consumer markets *** Develop brand name *** Develop brand awareness *** Maturity Advertising – – Trade promotions Customers are demanding product. – Product is being pulled through channel. Sales promotions – Consumer demand is already high. – Salespeople serve as order-takers. Differentiate brand *** ***Indicates high expenditures Advertising – Differentiate brand from competition *** – Push product through channel *** Encourage consumers to purchase *** – – – Encourage salespeople to push brand *** Differentiate brand *** Ineffective in pushing product in channel Sales promotions – Demand is declining. New technology is replacing product. Trade promotions Personal selling Personal selling – Sales promotions – Decline Trade promotions – Not effective Personal selling – Advertising – Sales promotions – Develop awareness *** Build industry demand *** Trade promotions – Growth Ineffective in stimulating demand Personal selling – Market is shrinking and limited Communication Budget Methods Objective-and-task Percent-of-sales Comparative parity Executive-judgment All-you-can-afford Measuring Communication Effectiveness - Is the sales growth or decline due to promotion, or is it attributable to other factors such as price, quality, or service? - Sales vs. Communication objectives/effects? Advertisement Evaluation • Concept and Copy Tests • Recall/Recognition and Attitude Tests Trade and Sales Promotion Evaluation • Sales changes • Inquiries • Redemption/Response rates Personal Selling Evaluation • • • • Sales Number of new customers Customer retention Customer satisfaction Global Communications Globally Integrated Marketing Communication is an international trend. The challenges to coordinate marketing efforts are the cultural difference. International companies have two strategies available: Standardization: The process of using the same product and marketing approach across countries Adaptation: The process of modifying the product and marketing approach for each country “Think globally but act locally.”