* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nerve activates contraction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
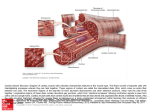
Muscle Tissue Muscle tissue is highly vascular & highly cellular Less matrix = more flexibility More blood flow = more ATP made Elongated shape Actin & myosin – contractile myofilaments Muscle Tissue Function is to produce movement Three types Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Slide 3.64 Muscle Tissue Types Skeletal muscle Voluntary control Cells attach to connective tissue Cells are striated (striped) Cells have more than one nucleus (multinucleate) Figure 3.19b Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Slide 3.65 Muscle Tissue Types Smooth muscle Involuntary muscle Surrounds hollow organs Attached to other smooth muscle cells No visible striations One nucleus per cell (uninucleate) Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 3.19a Slide 3.67 Muscle Tissue Types Cardiac muscle Found only in the heart Function is to pump blood (involuntary control) Cells attached to other cardiac muscle cells at intercalated disks and split at the bifurcations Bifurcation Cells are striated One nucleus per cell Figure 3.19c Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Slide 3.66 Nervous Tissue Consists of brain, spinal cord, nerves Carry electrical signals 2 major cell types: Neurons: generate & conduct electricity Usually nonregenerative Neuroglia: support neurons Brain tumors? Tissue Repair 1. Regeneration is the replacement of destroyed tissue by proliferation of the same type of cells. 2. Fibrosis is the replacement of destroyed tissue by connective (scar) tissue. 3. The major type of tissue repair that takes place is determined by: a. The type of tissue injured b. The severity of the injury Muscle, Nervous & Tissue Repair review