* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Stroop effect wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
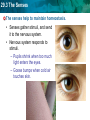
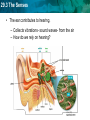
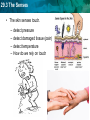
29.3 The Senses Sponge 7 Please write a short paragraph (3-4 sentences) explaining and giving examples of how drugs alter your brain chemistry. –Use the vocabulary: addiction, and tolerance, Stimulants or depressants 29.3 The Senses • Addiction: • physiological need for a substance – Examples? What does the addiction lead a person to do? • Tolerance: • Takes larger doses of the drug to produce the same effect – What is happening inside of their brain/body? • Stimulants: • are drugs that increase mental and physical functions (increase neurotransmitter and electrical signals) – Examples? Effects? • Depressants: • Cause fewer action potentials and decrease neurotransmitter – Examples? Effects ? 29.3 The Senses Objective • Today you will explain how the senses detect physical and chemical stimuli by taking The Stroop Effect Color Test. • What is stimuli? 29.3 The Senses Standard 9.e • Students know the roles of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons in sensation, thought, and response. 29.3 The Senses KEY CONCEPT The senses detect the internal and external environments. Name the five senses 29.3 The Senses • If I blindfolded you and place you in the back of the room would you reach the door? • Your sensory organs and your brain allow you to perceive stimuli as various sounds, sights, smells, and tastes 29.3 The Senses Reactions to stimuli Ex: Eyes react to bright or dim light by changing the size of your pupils. Ex: When your skin feels cold _________________. Other examples? 29.3 The Senses The senses help to maintain homeostasis. • Senses gather stimuli, and send it to the nervous system. • Nervous system responds to stimuli. – Pupils shrink when too much light enters the eyes. – Goose bumps when cold air touches skin. 29.3 The Senses The senses detect physical and chemical stimuli. • The eye contributes to vision • Humans rely on vision more than any of the other senses • Eye contains about 70% of all the sensory receptors in the body • Depends on the amount of light available “I can’t believe my eyes!” 29.3 The Senses • The ear contributes to hearing. – Collects vibrations- sound waves- from the air – How do we rely on hearing? 29.3 The Senses • Taste and smell are closely related. – Chemoreceptors detect chemicals dissolved in fluid. – How do we rely on taste and smell? 29.3 The Senses • The skin senses touch. – – – – detect pressure detect damaged tissue (pain) detect temperature How do we rely on touch 29.3 The Senses The Stroop Effect Color Test • Draw two columns on your paper • Pair up with a person sitting next to you Column #1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Column #2 29.3 The Senses Directions: • 8 colors will be shown to you • Say the COLOR of the word shown • Put a check mark in the column if they answered correctly first 29.3 The Senses Blue 29.3 The Senses Yellow 29.3 The Senses Red 29.3 The Senses Green 29.3 The Senses Black 29.3 The Senses Purple 29.3 The Senses Gray 29.3 The Senses Orange 29.3 The Senses Column #2 • Remember say the COLOR of the word shown 29.3 The Senses Red 29.3 The Senses Gray 29.3 The Senses Orange 29.3 The Senses Blue 29.3 The Senses Black 29.3 The Senses Yellow 29.3 The Senses Green 29.3 The Senses Purple 29.3 The Senses Score your partner: • How many out of 8 in the first and second column? • • • Same score? Different? Timing? • Hypothesize why the second list took you longer than the first list. 29.3 The Senses The Stroop Effect • Psychologist John Stroop studied the processing of words and how these thought processes affected other mental tasks. • He found that the brain must override an automatic response when it receives conflicting information, or interference 29.3 The Senses How much detail can you remember? 29.3 The Senses What can you remember? • How many people were in the picture? • 4 • What was the man reading the newspaper wearing? • Hat, green jacket • How many of the men had sunglasses? • 2- one wearing them, one hanging on shirt • Describe the man on the left. • Tan jacket, white shirt with a blue design, had a beard, white, blue eyes 29.3 The Senses Why can’t you remember some of the information? Our brain distinguishes between things that are important or not important when interacting with the environment. 29.3 The Senses 3 composite sketches by three witnesses 29.3 The Senses Write down the first picture you see in each optical illusion. 29.3 The Senses 29.3 The Senses 29.3 The Senses 29.3 The Senses 29.3 The Senses 29.3 The Senses 29.3 The Senses 29.3 The Senses 29.3 The Senses 29.3 The Senses 29.3 The Senses 29.3 The Senses 29.3 The Senses Review • Does your nose actually smell? • Does your tongue actually taste? • What is the major organ involved with your senses? • How might neurons be involved in this? • Remember the terms sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 29.3 The Senses Why didn’t you see more than one picture at first in the optical illusion? • Your brain is perceiving individual sensory stimuli as a meaningful whole. 29.3 The Senses Homework Search the internet for other optical illusions to share tomorrow Or Bring in a picture of people (not you) from a magazine, the internet, or an actual photo to share with your table to reenact the “witness” test