* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Marketing?
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Value proposition wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
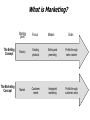
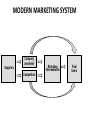
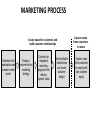
Introduction to Marketing: Value Exchange Process Prof Agus W. Soehadi PhD [email protected] Hugo Boss What is Marketing? Marketing is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion and distribution of ideas, goods and services to create exchanges (maintain relationship) that satisfy individual and organizational objectives (AMA 2004) Nike What is Marketing? Starting point Focus Means The Selling Concept Factory Existing products Selling and promoting Profits through sales volume The Marketing Concept Market Customer needs Integrated marketing Profits through customer value Ends Indo Mie MODERN MARKETING SYSTEM Suppliers Company (marketer) Competitors Marketing Intermediaries Final Users MARKETING PROCESS Create value for customers and build customer relationships Understand the marketplace and customer needs wants Design a customer-driven marketing strategy Construct an integrated marketing programs that delivers superior value Build profitable relationships and create customer delight Capture value from customers in return Capture value from customers to create profit and customer equity The Marketing Process • A simple model of the marketing process: – Understand the marketplace and customer needs and wants. • Design a customer-driven marketing strategy. – Construct a marketing program that delivers superior value. – Build profitable relationships and create customer delight. – Capture value from customers to create profits and customer quality. Gabbot (2004) Holcim Needs, Wants, & Demands • Need: State of felt deprivation including physical, social, and individual needs. – Physical needs: • Food, clothing, shelter, safety – Social needs: • Belonging, affection – Individual needs: • Learning, knowledge, self-expression Gabbot (2004) Needs, Wants, & Demands • Wants: Form that a human need takes, as shaped by culture and individual personality. • Wants + Buying Power = Demand Gabbot (2004) Need / Want Fulfillment • Needs and wants are fulfilled through a Marketing Offer: – Some combination of products, services, information, or experiences offered to a market to satisfy a need or want. Gabbot (2004) Need / Want Satisfiers • Products: – Persons – Places – Organizations – Information – Ideas • Services – Activity or benefit offered for sale that is essentially intangible and does not result in ownership. Brand Experiences: “. . . dazzle their senses, touch their hearts, stimulate their minds.” Gabbot (2004) Mercedes-Benz THE CONCEPT OF EXCHANGE (Why people buy?) Products Needs, wants, and demands Kotler (2006) Marketing as an exchange WHAT IS EXCHANGED • There are many definitions and models of how exchange takes place but importantly we must ask ‘what is being exchanged. – Meanings associated with exchange: - Utilitarian exchange Symbolic exchange Hedonic exchange Composite exchange Marketing as an exchange Utilitarian exchange • This type of exchange is referred to as economic exchange. Goods are given in return for money or other goods. Symbolic exchange • Symbolic exchange is an exchange where the transaction involves psychological or social characteristics. Marketing as an exchange Hedonic exchange • Hedonic exchange refers to an exchange where the transaction involves satisfying five senses Composite exchange • Composite exchange refers to an exchange that has both utilitarian and symbolic meaning. Starbucks Coffee Exchanging value • Holbrook extracts three key sources of customer value: – 1. Interaction – 2. Comparison – 3. Experience • Interaction, comparison and experience form a value system. Exchanging value Customer value is: • 1. A trade off between product quality and the price • 2. A trade off between a set of benefits and specific categories of costs • 3. The hierarchy of derived benefits obtained from particular product attributes when using the product • 4. The resulting emotional, practical and logical worth associated with the product • 5. A trade off between received value and desired value Conclusion Suppliers Company (marketer) Marketing Intermediaries Competitors Value Exchange Final Users