* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marketing Web Site
Web analytics wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Music industry wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Online advertising wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Online shopping wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
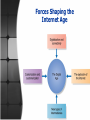
Marketing in Digital Age Dony Eko Prasetyo, S.IP. Amazon.com • • • • Started in July 1995 selling books One of the best known names on the Web Profitability has been a challenge Customer-driven company which strives to design the best customer experience on the Web • The first to use collaborative filtering technology for customer recommendations • With its slow earning, can its business model make it the Wal-Mart of the Web? Major Forces Shaping the Digital Age • Digitalization and Connectivity – The flow of digital information requires connectivity • Intranets, Extranets, and the Internet • The Internet Explosion – Key driver of the digital age – Using the Web to find information on major life decisions Major Forces Shaping the Digital Age Cont’d • New Types of Intermediaries – The click-and-mortar business model has been highly successful • Customization – Firms are individualizing their products, services, messages and media – True customization is when a consumer designs their own offering or product Forces Shaping the Internet Age Marketing in the Digital Age • What does this mean for: – Brochures & catalogs? – TV & radio advertising? – Banner ads? – E-newsletters? Marketing in the Digital Age • THE DIGITAL AGE • New tools = new strategies + tactics – Search – Web 2.0 – user-created content, feedback loops, blogs, social networks – Customer relationship management (CRM) Marketing in the Digital Age • THE DIGITAL AGE – What becomes possible? – What becomes unnecessary? – What trends are emerging? Marketing in the Digital Age • THE DIGITAL AGE - trends – Share of customer, not share of market – Smaller markets, higher saturation – Platforms for open development – Frictionless economy • Good-bye to middlemen, agencies – Disruptive innovation as a way of life Marketing in the Digital Age • THE DIGITAL AGE – is the age of search – Customers, partners, employers find you on: • Google, LinkedIn, Facebook, MySpace – Social networks put you in control of your online identity Marketing in the Digital Age • THE DIGITAL AGE – is the age of partnership and collaboration – Good customers are the advertisers – Bad customers are partners in quality control – Transparency and collaboration make the digital age a very public place • Wikipedia, Jigsaw, Yelp! Marketing in the Digital Age • THE DIGITAL AGE – is the age of disruptive innovation as a way of life – Platforms for development: • • • • I-phone apps Facebook apps Google apps Salesforce.com apps (computing cloud) Marketing in the Digital Age • THE DIGITAL AGE – is the age of intense customer focus – Waning terminology: • Market share/market segmentation • Target audience, ratings, demographics – Digital thinking: • Share of customer/share of wallet • Personal, customized, 1:1 Marketing in the Digital Age • THE DIGITAL AGE – is the age of intense customer focus – Focus on meeting customer needs…as many of them as are feasible • ABC Pest & Lawn • Dell • Google – Marketing & Sales are ONE Marketing Strategy in the Digital Age • • • Requires a new model for marketing strategy and practice. Some suggest that all buying and selling will eventually be done electronically. Companies need to retain old skills and practices but add new competencies. Marketing Strategy in the Digital Age • E-business: – uses electronic means and platforms to conduct business. Marketing Strategy in the Digital Age • E-commerce: – facilitates the sale of products and services by electronic means. E commerce Includes: • Online business to business transactions • Online business to consumer transactions • Digital delivery of products and services • Online merchandising • Automated telephone transactions eg phone banking • EFTPOS and other automated transfer systems Marketing Strategy in the Digital Age • E-marketing: – Includes efforts that inform, communicate, promote, and sell products and services over the Internet. Buyer Benefits of ECommerce • Convenience • Easy and private • Greater product access/selection • Access to comparative information • Interactive and immediate Seller Benefits of ECommerce • Relationship building • Reduced costt • Increased speed and efficiency • Flexibility • Global access E Commerce Domain B2C (Business to Consumer) • The online selling of goods and services to final consumers. There is increasing diversity in buyers. • – • This provides increasing opportunities for targeting markets. Is customer initiated and controlled. B2B (Business to Business) • • • • By 2005, more than 500,000 enterprises will participate as buyers, sellers, or both. Most major B2B marketers offer product information, purchasing, and support services online. Open trading exchanges—huge specialty e-marketspaces to conduct transactions. More private trading networks being developed. C2C (Consumer to Consumer) • • • Occurs on the Web and includes a wide range of products and services. Forums: discussion groups located on commercial online services. Newsgroups: the Internet version of forums. C2B (Consumer to Business) • Consumers can search out sellers, view offers, initiate purchases, and give feedback. – Example: on priceline.com one can bid for airline tickets, hotel rooms, etc. and decide whether to accept company offers. Click-Only Companies • • • • • • E-tailers Search engines and portals Internet service providers Transaction sites Content sites Enabler sites Reasons for dot.com Failures • • • • Poor research or planning. Relied on spin and hype instead of marketing strategies. Spent too heavily on brand identities. Devoted too much effort to acquiring new customers instead of building loyalty. Click-and-Mortar Companies • Most established companies resisted adding Web sites because of the potential for channel conflict and cannibalization. Many are now doing better than clickonly companies. Reasons: • • – – – – – Trusted brand names and more resources Large customer bases More knowledge and experience Good relationships with suppliers Can offer customers more options Setting up for E-Marketing •Creating websites •Placing online ads and promotions •Creating or using Web communities •Using E-mail Creating websites •Corporate websites – Build goodwill and relationships; generate excitement •Marketing websites – Engage consumers and attempt to influence purchase •Website design – 7 C’s of effective website design Types of Web Sites • • • • Corporate Web Site: Designed to build customer goodwill and supplement other sales channels. Offers information to customers. Builds closer customer relationships. Generates excitement about the company. Types of Web Sites • • Marketing Web Site: Engages consumers in an interaction that moves them closer to a direct purchase. Provides information about the products. Seven C’s of Website Design •Context •Content •Community •Communication •Connection •Commerce Customization Placing online ads and promotions •Online forms of ads and promotions •Future of online ads Online Ads and Promotion • Forms of online advertising & promotion: – – – – – – – Banner ads & tickers (move across the screen) Skyscrapers (tall, skinny ads at the side of a page) Rectangles (boxes that are larger than a banner) Interstitials (pop up between changes on Web site) Content sponsorships (sponsoring special content) Microsites (limited areas paid for by an external company) Viral marketing (Internet version of word-of-mouth) The Future of Online Advertising • Web communities: – • Allows members to congregate online and exchange views on issues of common interest E-mail: – – – Use of “enriched” e-mail messages Backlash against spam can be problem Allow people to opt-out of promotions Creating or using Web communities •Web communities allow members with special interests to exchange views – Social communities – Work-related communities •Marketers find well-defined demographics and shared interests useful when marketing Using E-mail •E-mail marketing – Key tool for B2B and B2C marketing – Clutter is a problem – Enriched forms of e-mail attempt to break through clutter – Spam is a problem Promise and Challenges of E-Commerce • The Promise of E-Commerce – Online marketing will become a successful business model for some companies – The question is “how,” not “whether,” to deploy Internet technology – The Internet should be used as one approach or tool in the fully integrated marketing mix Legal and Ethical Issues • • • • • Online privacy Online security Internet fraud Segmentation and discrimination Access by vulnerable or unauthorized groups