* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marketing Is All Around Us
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
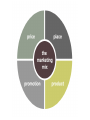
Marketing Is All Around Us Quick Think • How would you define Marketing? • Activities that fall under its umbrella The Marketing Umbrella Marketing • Marketing is the process of planning, pricing, promoting, selling and distributing ideas, goods, or services to create exchanges that satisfy customers Marketing • As a marketer, you need to keep up with trends and consumer attitudes • The products, ideas or services you develop and the way you price, promote and distribute them should reflect those trends and attitudes Ideas, Goods & Services • • Goods are tangible items that have monetary value and satisfy needs • Cars, toys, furniture, tv’s, etc. Intangible items that have monetary value and satisfy your needs are services • • You cannot physically touch them Cooking, cutting hair, movie theaters, etc. 7 Marketing Core Functions 1. Channel Management • a.k.a. Distribution • The process of deciding how to get goods into customer’s hands • Methods of transportation • Tracking & storing 7 Marketing Core Functions 2. Market Planning • Involves understanding the concepts and strategies used to develop and target specific marketing strategies to a select audience • Collection of data, data analysis, using that data for a marketing plan 7 Marketing Core Functions 3. Marketing Information Management • Gathering information & storing it about customers, trends and competing products • • Research done on a continual basis Companies conduct research so they can be successful at marketing their products 7 Marketing Core Functions 4. Pricing • Dictates how much to charge for goods and services in order to make a profit • Based on costs and what competitors are charging • Must determine how much customers are willing to pay 7 Marketing Core Functions 5. Product/Service Management • Obtaining, developing, maintaining, and improving a product or a product mix in response to market opportunities • Research guides this toward what the consumer needs and wants 7 Marketing Core Functions 6. Promotion • The effort to inform, persuade or remind potential customers about a business’s product or services • Television, radio, etc. 7 Marketing Core Functions 7. Selling • Provides customers with the goods and services they want • Retail and business-to-business • Techniques include determining clients needs & wants and responding through communication The Marketing Concept • The idea that a business should strive to satisfy customers’ needs and wants while generating a profit for the firm • The focus is on the customer Economic Benefits of Marketing • Marketing plays an important role in an economy because it provides the means for competition to take place • New & improved products • Lower prices Market • All people who share similar needs and wants and who have the ability to purchase a given product are called a market Consumer v. Industrial Market • Consumer market consists of consumers who purchases goods and services for personal use (business-toconsumer / B2C) • Industrial market (business-to-business / B2B) market includes all businesses that buy products for use in their operations Market Share • A market is further described by the total sales in a product category • Camera market, video game market, etc. • A company’s percentage of total sales in a given market is its market share Target Market & Market Segmentation • Market segmentation is the process of classifying customers by needs and wants • The goal of this is to identify the group of people most likely to become customers Target Market & Market Segmentation • The group that is identified for a specific marketing program is the target market • Target markets are very important because all marketing strategies are directed to them Consumers v. Customers • A product may have more than one target market • Children’s cereal • Children (consumers) • Parents (customers) • Ad’s will try to reach both children & parents Customer Profile • To develop a clear picture of their target market, businesses create a customer profile • Lists information about the target market, such as: • age, income level, ethnic background, occupation, attitudes, lifestyle and geographic residence The Marketing Mix • The marketing mix includes four basic market strategies called the four P’s • Product • Place • Price • Promotion The Marketing Mix • Product • Choosing what products to make and sell • Product design, features, brand name, packaging, service and warranty The Marketing Mix • Place • The means of getting the product into the consumer’s hands is the place factor of the marketing mix • Knowing where one’s customers shop • Determines how and where a product will be distributed The Marketing Mix • Price • What is exchanged for the product • Price strategies should reflect what customers are willing and able to pay • Takes into account competition The Marketing Mix • Promotion • Refers to activities related to advertising, personal selling, sales promotion and publicity • How potential customers are told about the product