* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Competition (companies) wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
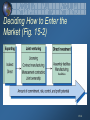
Chapter 15 The Global Marketplace 15-1 Road Map:Previewing the Concepts Discuss how the international trade system, economic, political-legal, and cultural environments affect a company’s international marketing decisions. Describe three key approaches to entering international markets. Explain how companies adapt their marketing mixes for international markets. Identify the three major forms of international marketing organization. 15-2 Global Marketing into the Twenty-First Century The world is shrinking rapidly with the advent of faster communication, transportation, and financial flows. International trade is booming and now accounts for a quarter of the United States’ GDP. Between 1996 and 2006, U.S. exports are expected to increase 51%. Global competition is intensifying and few U.S. industries are now safe from foreign competition. 15-3 Global Marketing into the Twenty-First Century To compete, many U.S. companies are continuously improving their products, expanding into foreign markets, and becoming global firms. Global firms face several major problems: High debt, inflation, and unemployment have resulted in highly unstable governments & currencies, Governments placing more regulations on foreign firms, Protectionist tariffs and trade barriers, Corruption. 15-4 McDonald’s in Beijing Many U.S. companies have long been successful, including McDonald’s, at international marketing. http://www.mcdonalds. com/ 15-5 Major International Marketing Decisions (Fig. 15-1) 15-6 Looking at the Global Marketing Environment The International Trade System i.e. Tariff, Quota, Embargo, Exchange Control, and Nontariff Trade Barriers The World Trade Organization and GATT Treaty designed to promote world trade by reducing tariffs and other international trade barriers Regional Free Trade Zones Group of nations organized to work toward common goals in the regulation of international trade 15-7 When exporting goods to a foreign country, a marketer may be faced with trade restrictions. Discuss the effects that a tariff might have on an exporter’s marketing mix. 15-8 Economic Environment Subsistence Economies Industrial Economies Types of Industrial Structure Raw Material Exporting Economies Industrializing Economies 15-9 Political-Legal Environment At Least Four Political-Legal Factors Should be Considered in Deciding Whether to do Business in a Given Country: Attitudes Toward International Buying Government Bureaucracy Monetary Regulations Political Stability 15-10 Cultural Environment Sellers Must Examine the Following Before Planning a Marketing Program Within a Given Country. How Customers Think About and Use Products Cultural Traditions, Preferences, and Behaviors Business Norms and Behavior 15-11 Deciding Whether to Go International Reasons companies might consider international expansion: Global competitors attacking the domestic market, Foreign markets might offer higher profit opportunities, Domestic markets might be shrinking, Need an enlarged customer base to achieve economies of scale, Reduce dependency on any one market, Customers might be expanding abroad. Most companies do not act until some situation or event thrusts them into the global arena. 15-12 Deciding Which Markets to Enter Define Organization’s Marketing Objectives and Policies What Volume of Foreign Sales is Desired? How Many Countries Should the Firm Go Into? What Types of Countries Should be Entered? Rank by Market Size & Growth, Cost of Doing Business, Competitive Advantage, & Risk Level. 15-13 Deciding How to Enter the Market (Fig. 15-2) 15-14 Pair with the student on your left to discuss the following situation. Once a company has decided to sell in a foreign country, it must determine the best mode of entry. Assume that you were the marketing manager for Mountain Dew and devise a plan and pick a mode of entry for marketing your product in China. 15-15 Adapted Marketing Mix Adjusts the Marketing Mix Elements to Each International Target Market. i.e. Japanese Barbie Changes in Product, Advertising, Distribution Channels, & Price Deciding on the Global Marketing Program Standardized Marketing Mix Selling Largely the Same Products and Using the same Marketing Approaches Worldwide . i.e Coca-Cola 15-16 Five Global Product and Promotion Strategies (Fig. 15-3) 15-17 International Pricing Companies face many problems in setting their international prices. Possibilities in setting prices include: Charge a uniform price all around the world. Charge what consumers in each country could pay. Use a standard markup of its costs everywhere. International prices tend to be higher than domestic prices because of price escalation. Companies may become guilty of dumping – when a foreign subsidiary charges less than its costs or less than it charges in its home market. 15-18 Whole-Channel Concept for International Marketing (Fig. 15-4) 15-19 Deciding on the Global Marketing Organization 1. Organize an Export Department 2. Create an International Division 3. Become a Global Organization Degree of Involvement in International Marketing Activities 15-20 Rest Stop: Reviewing the Concepts Discuss how the international trade system, economic, political-legal, and cultural environments affect a company’s international marketing decisions. Describe three key approaches to entering international markets. Explain how companies adapt their marketing mixes for international markets. Identify the three major forms of international marketing organization. 15-21