* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 1
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Brand loyalty wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Yield management wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
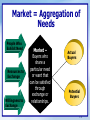
Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Chapter 1 c Amazon Strong sales, no profits Customer-driven to its core Each customer’s experience is unique Provides great selection, good value, discovery as well as convenience A true online community 1-1 Objectives Be able to define marketing and discuss its core concepts. Be able to define marketing management and compare the five marketing management orientations. 1-2 Objectives Understand customer relationship management and strategies. Realize the major challenges facing marketers in the new “connected” millennium. 1-3 Why Study Marketing? You are paying a lot for it. it is estimated that marketing costs consumers 50 cents of each dollar spent. It effects almost every aspect of your daily life Your future job requires that you work with marketers - What is Marketing? Process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products and value with others. Simply put: Marketing is the delivery of customer satisfaction at a profit. 1-5 What is Marketing? Marketing is managing profitable customer relationships Attracting new customers Retaining and growing current customers “Marketing” is NOT synonymous with “sales” or “advertising” 1-6 What Can Be Marketed? Goods Services Places Ideas Events Persons Properties Organizations Information Experiences What is being marketed in this ad? 1-7 Core Marketing Concepts* (Fig. 1-1) Markets Needs, wants, and demands Value, satisfaction, and quality Products and services Exchange, transactions, and relationships 1-8 What are Consumer’s Needs, Wants and Demands? Needs - state of felt deprivation for basic items such as food and clothing and complex needs such as for belonging. i.e. I am hungry. Wants - form that a human need takes as shaped by culture and individual personality. i.e. I want a hamburger, French fries, and a soft drink. Demands - human wants backed by buying power. i.e. I have money to buy this meal. 1-9 Types of Need physical needs food, clothing, shelter social needs belonging, acceptance individual needs knowledge, self-esteem Market = Aggregation of Needs Resources to Exchange Willingness to Exchange Market – Ethical Buyers who share a particular need or want that can be satisfied Attitudes through of exchange Others or relationships. Unexpected Situational Factors People Who Exhibit Need Actual Buyers Potential Buyers 1 - 11 What Will Satisfy Consumer’s Needs and Wants? Products Anything that can be Offered to a Market to Satisfy a Need or Want Experiences Persons Organizations Information Places Ideas Services Activities or Benefits Offered for Sale That Are Essentially Intangible and Don’t Result in the Ownership of Anything 1 - 12 How Do Consumers Obtain Products and Services? Exchanges Transactions Relationships* Relationship Marketing: Text page 11 How does Saturn build lasting relationships with customers? Building a Marketing Network Consisting of The Company and All Its Supporting Stakeholders Click or Press Space Bar to Return 1 - 13 Exchange* something for something: QUID PRO QUO - a basic concept in marketing requires at least two parties each must have something of value to the other Free to accept/reject the offer Must be able to communicate and deliver No Exchange = Self Sufficiency If you can produce everything you need you don't need exchange .... Hermits, Old Order Oregonians, Survivalist How Do Consumers Choose Choose Among Products and Services? Value Gained From Owning a Product and Costs of Obtaining the Product is Customer Value Product’s Perceived Performance in Delivering Value Relative to Buyer’s Expectations is Customer Satisfaction Customer Loyalty 1 - 16 Figure 1-2: Elements of a Modern Marketing System 1 - 17 Marketing Management Marketing management is “the art and science of choosing target markets and building profitable relationships with them.” Creating, delivering and communicating superior customer value is key. 1 - 18 Marketing Management Customer Management: Marketers select customers that can be served well and profitably. Demand Management: Marketers must deal with different demand states, ranging from no demand to too much demand. 1 - 19 Marketing Management Production Concept Management Orientations Selling Concept Product Concept Marketing Concept Societal Marketing Concept 1 - 20 Figure 1-3: The Selling and Marketing Concepts Contrasted 1 - 21 Figure 1-4: Considerations Underlying the Societal Marketing Concept 1 - 22 Figure 1-5: Relationship Between Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty 1 - 23 CRM Customer relationship management (also called CRM) is defined as: “the overall process of building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction.” 1 - 24 CRM It costs 5 to 10 times MORE to attract a new customer than it does to keep a current customer satisfied. Marketers must be concerned with the lifetime value of the customer. 1 - 25 BusinessNow SatMetrix Video Clip View what the experts have to say about customer loyalty and the bottom line. Click the picture above to play video 1 - 26 CRM Key Concepts Attracting, retaining and growing customers Building relationships and customer equity Customer value and satisfaction Perceptions are key Created by meeting/ exceeding expectations Loyalty and retention Many benefits of loyalty Increases as satisfaction levels increase Delighting consumers should be the goal Growing customer share Cross-selling 1 - 27 CRM Key Concepts Attracting, retaining and growing customers Building relationships and customer equity Customer equity Total combined customer lifetime values of all customers Measures firm’s performance, but in a manner that looks to the future 1 - 28 CRM Key Concepts Attracting, retaining and growing customers Building relationships and customer equity Customer relationship levels and tools Target market typically dictates type of relationship Basic relationships Full relationships Customer loyalty and retention programs Adding financial benefits Adding social benefits Adding structural ties 1 - 29 Marketing Challenges Technological advances, rapid globalization, and continuing social and economic shifts are causing marketplace changes. Major marketing developments can be grouped under the theme of Connecting. 1 - 30 Figure 1-6: Today’s Marketing Connections 1 - 31 Marketing Challenges Connecting Via technology With customers With marketing partners With the world Advances in computers, telecommunications, video-conferencing, etc. are major forces Databases allow for customization of products, messages and analysis of needs The Internet Facilitates anytime, anywhere connections Facilitates CRM Creates marketspaces 1 - 32 Marketing Challenges Connecting Via technology With customers With marketing partners With the world Selective relationship management is key Customer profitability analysis separates winners from losers Growing “share of customer” Cross-selling and upselling are helpful Direct sales to buyers are growing 1 - 33 Marketing Challenges Connecting Via technology With customers With marketing partners With the world Partner relationship management involves: Connecting inside the company Connecting with outside partners Supply chain management Strategic alliances 1 - 34 Marketing Challenges Connecting Via technology With customers With marketing partners With the world Globalization Competition New opportunities Greater concern for environmental and social responsibility Increased marketing by nonprofit and public-sector entities Social marketing campaigns 1 - 35 Connecting with Values . . . The Body Shop Visit the “Our Values” and “About Us” sections of The Body Shop’s web site. How might the values espoused by the company influence the manner in which the Body Shop . . . The Body Shop • • • • Chooses their strategic partners? Advertises fragrances to consumers? Develops new products? How might these decisions in turn impact “the bottom line”? 1 - 36