* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Promotion Management
Advertising management wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
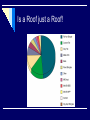
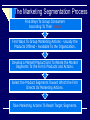
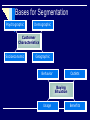
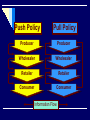
Chapter 2 The Role of IMC in the Marketing Process Last Class Introduction to IMC Links to marketing and promotional elements Today’s Objectives Role of IMC in Marketing What kind of a strategy is Samsung using to compete against Sony? a repositioning strategy niche market strategy a concentrated market strategy an undifferentiated market strategy lifestyle segmentation What is? A market opportunity A competitive advantage A market threat Marketing to a Lifestyle + The Role of IMC in Marketing Nike’s and Reebook’s success : they recognize their business is no longer about just selling shoes. It’s about selling sports, entertainment, style, and fashion. Tell me about other brands… What business are they in? Kale Duru Nivea The Target Marketing Process Identify markets with unfulfilled needs Determining market segmentation Selecting market to target Positioning through marketing strategies Is a Roof just a Roof! Different products for different needs! The Marketing Segmentation Process Find Ways To Group Consumers According According To To Their Their Needs. Needs Find Ways To Group Marketing Actions - Usually the Products Offered - Available To the Organization. Develop a Market/Product Grid To Relate the Market Segments To the Firm’s Products and Actions. Select the Product Segments Toward Which the Firm Directs Its Marketing Actions. Take Marketing Actions To Reach Target Segments. Bases for Segmentation Psychographic Demographic Customer Characteristics Socioeconomic Geographic Behavior Outlets Buying Situation Usage Benefits Hispanics Prefer Spanish Language Ads Six Positioning Questions 1. What position do we have now? 2. What position do we want to own? 3. From whom must we win this position? 4. Do we have the money to do the job? 5. Do we have the tenacity to stay with it? 6. Does our creative strategy match it? What is this? The first production Model T Ford was built on September 27, 1908. Ford continued building the "T" for the next 19 years, until it was replaced by the Model "A" in 1928. Ford Motor Company Positioning Strategies How should we position? By Attributes and Benefits? By Price or Quality? By Use or Application? By Product Class? By Product User? By Competitor? By Cultural Symbols? Positioning Strategy Development Process 1. Identify the competitors 2. Assess perceptions of them 3. Determine their positions 4. Analyze consumer preferences 5. Make the positioning decision 6. Monitor the position Developing a Positioning Strategy Attribute/benefit Price/quality Use/application Product class Product users Competitor Cultural symbol Repositioning - Energizer Ikea Baking Soda Butter or margarine Nike Sana vs. Aymar, 7UP CocaCola in Ramadan Volvo Product Decisions A product is a bundle of benefits or values. Product quality, branding, packaging, and company name contribute to product image. Branding and Packaging Work Closely Together Product Decisions BRANDING Brand name communicates attributes and meaning Advertising creates and maintains brand equity PACKAGING Packaging has become increasingly important It’s often customers’ first exposure to product A Package Is More than a Container + Packaging Enhances Brand Identity For other products? Which one is more expensive? Pricing Decisions consistent with perceptions of the product. Higher prices ------------ higher product quality. Lower prices reflect bargain or “value” perceptions Price, advertising and distribution be unified in identifying the product position Distribution Channel Decisions Channel decisions involve: Selecting Managing Motivating -Independent intermediaries: Wholesalers Distributors Brokers Retailers Promotion to Push Goods Through Channels vs Promotion to Pull Goods Through Channels PUSH PULL Push Policy Pull Policy Producer Producer Wholesaler Wholesaler Retailer Retailer Consumer Consumer Information Flow Promotion to Push Goods Through Channels PUSH Point of Sale Displays, Racks, Stands Trade Deals, Special Displays Dealer Premiums, Prizes, Gifts Cooperative Advertising Deals Advertising Materials, Mats, Inserts Push Money or “Spiffs" Collaterals, Catalogs, Manuals Company Conventions, Meetings Promotion to Pull Goods Through Channels PULL Sampling, free trial Cents-off promotions Cents-off coupons Combination offers Premiums or gifts Contests, sweepstakes Point-of-purchase Trading stamps Push strategies involve promoting the product only to the next link down the distribution channel; advantage : cheap and relatively straightforward, and Not consumer-orientated. Techniques used: Point of sale displays, racks, stands Trade deals, special displays Dealer premiums, prizes, gifts Cooperative advertising deals etc Pull Strategies Focuses on consumer, aimed at the final consumers Most launch strategies would involve elements of both push and pull. Techniques used: Sampling, free trial Cents-off promotions Cents-off coupons etc. Next Class Organizing for Advertising and Promotion Read Chapter 3!!!