* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1: An Introduction to Consumer Behavior
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Online shopping wikipedia , lookup
Brand loyalty wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Targeted advertising wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
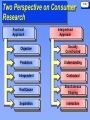
1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Consumer Behavior 1-2 “Remember Me?” 1-3 I'm the fellow who goes into a restaurant, sits down and patiently waits while the waitresses do everything but take my order. I'm the fellow who goes into a department store and stands quietly while the sales clerks finish their little chitchat. I'm the man who drives into a gasoline station and never blows his horn, but waits patiently while the attendant finishes reading his comic book. "Yes, you might say, I'm a good guy. But do you know who else I am? I am the fellow who never comes back, and it amuses me to see you spending thousands of dollars every year to get me back into your store, when I was there in the first place, and all you had to do to keep me was to give me a little service; show me a little courtesy." Source: From a Better Business Bureau bulletin submitted by An Arkansas Reader to Dear Abby Defining Consumer Behavior 1-4 Consumer Behavior is the Process Involved When Individuals or Groups Select, Use, or Dispose of Products, Services, Ideas or Experiences (Exchange) to Satisfy Needs and Desires. 1-5 Issues During Stages in the Consumption Process Consumers’ Impact on Marketing Strategy 1-6 • Understanding consumer behavior is good business. –Firms exist to satisfy consumers’ needs, so –Firms must understand consumers needs to satisfy them. • The Process of Marketing Segmentation: –Identifies Groups of Consumers Who are Similar to One Another in One or More Ways, and –Devises Marketing Strategies that Appeal to One or More of These Groups. 1-7 Segmenting Consumers by Demographic Dimensions Demographics are Statistics That Measure Observable Aspects of a Population Such As: Geography Race and Ethnicity Social Class and Income Age Gender Family Structure Consumers’ Impact On Marketing Strategy: Building Bonds With Consumers 1-8 • Relationship Marketing occurs when a company makes an effort to interact with customers on a regular basis, and gives them reasons to maintain a bond with the company over time. • Database Marketing involves tracking consumers’ buying habits very closely, and crafting products and messages tailored precisely to people’s wants and needs based on this information. Marketing’s Impact on Consumers: The Meaning of Consumption Types of Relationships a Person May Have With a Product: Self-Concept Attachment Helps to Establish the User’s Identity Nostalgic Attachment Serves as a Link With a Past Self Interdependence Part of the User’s Daily Routine Love Elicits Bonds of Warmth, Passion, or Other Strong Emotion 1-9 Marketing’s Impact on Consumers: Consumption Typology Explores the Different Ways Consumption Typology 1-10 That Products and Experiences Can Provide Meaning to People. There Are 4 Distinct Types of Consumption Activities: Consuming as Experience An Emotional or Aesthetic Reaction to Consumption Objects Consuming as Integration Express Aspects of Self or Society Consuming as Classification Communicate Their Association With Objects, Both to Self/ Others Consuming as Play Participate in a Mutual Experience and Merge Self With Group 1-11 Marketing’s Impact on Consumers – Marketing and Culture • Popular Culture – Intangible and Tangible Objects – The Global Consumer • Global Consumer Culture – Virtual Consumption • Business to Consumer Selling (B2C Commerce) • Consumer to Consumer Selling (B2B Commerce) • Virtual Brand Communities – Blurred Boundaries: Marketing and Reality Marketing Ethics 1-12 Business Ethics are Rules of Conduct That Guide Actions in the Marketplace - the Standards Against Which Most People in a Culture Judge What is Right and What is Wrong, Good or Bad. Other Marketing Ethics Issues 1-13 • Do Marketers Create Artificial Needs? – Response: Marketing attempts to create awareness that these needs do exist, rather than to create them. • Are Advertising and Marketing Necessary? – Response: Yes, if approached from an information dissemination perspective. • Do Marketers Promise Miracles? – Not if they are honest; they do not have the ability to create miracles. The Dark Side of Consumer Behavior 1-14 Compulsive Consumption Addictive Consumption >Behavior is Not Done by Choice >Gratification is Short-Lived >Strong Feelings of Regret or Guilt Afterwards > Gambling Illegal Activities Consumed Consumers > Consumer Theft (Shrinkage) >Anti-consumption – Culture Jamming – Cultural Resistance > People Who Are Exploited for Commercial Gain in the Marketplace. Interdisciplinary Influences Individual Focus Experimental Psychology Clinical Psychology Developmental Psychology Human Ecology Microeconomics Social Psychology Sociology Macroeconomics Semiotics/Literary Criticism Demography History Cultural Anthropology Social Focus 1-15 Two Perspective on Consumer Research Positivist Approach Interpretivist Approach Objective Socially Constructed Prediction Understanding Independent Contextual Real Cause Simultaneous Shaping Separation Interaction 1-16 Taking it From Here: The Plan of the Book 1-17 • Section II: Consumers As Individuals • Section III: Consumers As Decision Makers • Section IV: Consumers and Subcultures • Section V: Consumers and Culture The Wheel of Consumer Behavior 1-18