* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download International Business
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Brand equity wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Brand ambassador wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Pricing science wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
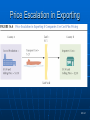
International Marketing 16-1 Chapter Preview • Introduce techniques for assessing sizes for given countries Contrast policies of standardized versus differentiated marketing programs for each country in which sales are made • Identify the five international communication strategies • Describe each element that impacts international distribution strategies • Identify various international pricing strategies and the factors that influence selection Forecasting Demand • Per capita consumption 16-5 Forecasting Potential Demand Additional variables • Obsolescence and leapfrogging of products • Costs – essential vs nonnecessity • Income elasticity – necessity vs discretionary • Substitution • Income inequality • Cultural factors and taste 16-4 Gap Analysis Method for estimating a company’s potential sales by identifying market segments it is not serving adequately When sales are lower than the estimated market potential for a product, the company has potential for increase sales Types of gaps • • • • Usage Competitive Product line distribution 16-6 Gap Analysis 16-7 Reasons to Penetrate Markets Country’s size Growth potential Proximity to home operations Stability of currency Political stability Orientations (Product policy) • • • • • Production Sales Customer Strategic marketing Societal marketing 16-9 Globalization and Marketing Standardized product and promotion Adapted product and/or marketing • Consistent image and message • Respond well to local needs • Contain costs • Obey local laws National Business Environments Cultural differences Laws and regulations National image Counterfeit goods Brand and Product Names Brand name Competitive advantage Consistent image Consider connotation Product name Select carefully Respect cultures Obey local laws International Branding Decisions Brand versus no brand Manufacturer’s brand versus private brand One brand versus multiple brands Worldwide brand versus multiple brands Issues: • • • • Language differences Expansion by acquisition Nationality images Laws concerning generic names 16-15 Product Life Cycles Consecutive market introductions Technology and travel make obsolete New-product development efforts Result is shorter product life cycles Push and Pull Strategies Push Strategy Pull Strategy Pressure channel members to carry a Create buyer demand that will encourage product and promote it to final users channel members to stock a product Choosing Push or Pull Powerful channel members make push difficult Fewer media outlets in emerging markets makes pull difficult Brand loyalty makes pull easier Marketing Communications • Process of sending promotional messages about products to target markets The Communications Mix Advertising • any paid form of nonpersonal presentation by a sponsor Personal Selling • personal presentations by a firm’s sales force Sales Promotion • short term incentives to encourage sales Public Relations • building good relations with various publics Direct Marketing • short term incentives to encourage sales Communication Strategy I Extend product and communications Global Simple and Luxury items consumer profitable goods Communication Strategy II Extend product / adapt communications Satisfies Serves Appeals to different need different function different buyer Communication Strategy III Adapt product / extend communications Local infrastructure Local content laws Can be costly Communication Strategy IV Adapt product and communications Rather uncommon Can be expensive Requires large profitable segment Communication Strategy V Product invention Purchasing power Economic development level Varying infrastructure Distribution Strategy Planning, implementing, and controlling the physical flow of a product from origin to consumption Physical goods Consulting services News providers Distribution Channels Degree of exposure Exclusive channel • One / few resellers Intensive channel • Many resellers Channel length Number of intermediaries Cost implications Product Characteristics Value density Product’s value relative to its weight and volume The lower a product’s value density, the more localized is its distribution system Distribution Problems Lack of market understanding Theft and corruption Financial loss Strategic impact Pricing Strategy Must match overall firm strategy Low-cost leadership Differentiation Focus Worldwide Pricing Single selling price for all international markets Difficulties • Local production cost • Export, distribution cost • Local purchasing power • Exchange rates Dual Pricing Different selling price abroad than at home • Price escalation • Lower local price Separate international from domestic buyers • If not, arbitrage possible Pricing Issues Transfer price Intra-company transfer Arm’s length price Free-market price Price controls Upper or lower limits Dumping Unfairly-low export price International Pricing Issues Different degrees of governmental involvement Greater diversity of markets Price escalation for exports Changing values of currency Differences in fixed versus variable pricing practices Retailers’ strength with suppliers 16-11 Price Escalation in Exporting 16-12