* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Brand loyalty wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
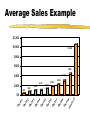
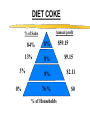
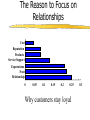
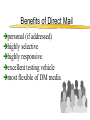
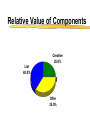
Marketing in CRM © 2006 Brian Broadway "The purpose of business is to create and keep a customer." Theodore Levitt, The Marketing Imagination Lester Wunderman said: “People don’t want quarter inch drill bits. They want quarter inch holes.” The Underlying Premises Premise 1 the single most important asset of your company is . . . Your Customers! Average Sales Example $1,200 $1,000 $1,062 $800 $600 $453 $310 $400 $113 $200 $84 $105 2 3 $192 $229 $145 $44 $0 ile c De 1 ile c De ile c De ile c De 4 ile c De 5 ile c De 6 ile c De 7 ile c De 8 9 10 le i e l c ci e e D D Premise 2 not all customers are created equal The Pareto Principle DIET COKE Annual profit % of Sales 84% 13% 3% 0% 8% 8% $59.15 $9.15 8% $2.11 76 % $0 % of Households Premise 3 it costs more to acquire a new customer than to keep an existing customer The Reason to Focus on Relationships Cost Reputation Products Service/Support Expectations None Relationship 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 Why customers stay loyal 0.3 The Ad Spend Disconnect* Internet Magazines Time Spent Radio Ad Spending Newspapers TV 0% 10% *The Economist, April 2, 2005 20% 30% 40% Concepts and Definitions Marketing Concept Satisfying want or need (at a profit) of customers Satisfying through mutually beneficial exchange The Evolution of Customers* Persuading Transacting Groups of Buyers with Individual Buyers Bonds with Lifetime Customers Customers as CoCreators Time Frame 1970s-1980s Late 1980s to early 1990s 1990s Beyond 2000 Managerial Mind-set Customer is an average statistic Customer is an individual statistic Customer is a person Customer is individual & part of social group Interaction Market Research Shift from Selling to helping Provide for customers based on observations Co-developers Communication One-way, targeted groups Databased communication Relationship marketing Active dialogue *Co-opting Customer Competence, Prahalad & Ramaswamy, HBR on Customer Relationship Management Permission Marketing Definition permission marketing Marketing centered around obtaining customer consent to receive information from a company. Coined and popularized by Seth Godin, permission marketing is the opposite of traditional interruption marketing. Permission marketing is about building an ongoing relationship of increasing depth with customers. In the words of Seth Godin, "turning strangers into friends, and friends into customers." Permission marketing has been hailed as a way for marketers to succeed in a world increasingly cluttered with marketing messages 1to1 Definition Focused on the individual customer, one-to-one marketing is based on the idea of an enterprise knowing its customer. Through interactions with that customer the enterprise can learn how he or she wants to be treated. The enterprise is then able to treat this customer differently than other customers. However, one-to-one marketing does not mean that every single customer needs to be treated uniquely; rather, it means that each customer has a direct input into the way the enterprise behaves with respect to him or her. http://www.1to1.com/Glossary.aspx#O CRM Customer Relationship Marketing is a practice that encompasses all marketing activities directed toward establishing, developing, and maintaining successful customer relationships. The focus of relationship marketing is on developing long-term relationships and improving corporate performance through customer loyalty and customer retention. Why Have a Relationship? •Customers expect: • excellence in products • excellence in service •A Competitive Advantage • excellence in building and maintaining customer relationships Interactive/CRM vs Traditional Marketing* Interactive Marketing Direct selling to individuals Medium is the marketplace Marketing controls process through to delivery Ads used to generate response Customers assume more risk Products delivered direct to consumer *Contemporary Direct Marketing, Spiller & Baier Traditional Marketing Mass selling to broad groups Retail is the marketplace Marketing loses control at distribution (channels) Ads used to build awareness Customers perceive less risk Consumer must deliver themselves to the product Segmentation Key Concepts of Marketing Strategy There are three components of a traditional marketing strategy: Marketing Strategy Segmentation Targeting Positioning Segmentation Segmentation divides the market into useful sub-units of similar consumers based on: Demographics – Geography – Psychographics – Cognitive and behavioral attributes – Bases for Segmenting Consumer Markets Demographic and socioeconomic Age, gender, marital status, household size, household lifecycle; religion, race/ethnic group, nationality, income, occupation, education, social class, asset ownership Geographic Country, region, population density, population size, climate Bases for Segmenting Consumer Markets (cont’d) Behavioural and situational User status, loyalty status, usage rate, purchase occasion, buyer readiness Psychological and psychographic Personality, motivation and needs, consumer attitude, lifestyle Benefits sought Time-savers, self-improvement Interactive/CRM Segmentation Behaviour Purchases, payments, media used by customer Collected Information Surveys, preferences, Analysis by Modeling Regression, neural networks, etc Target Marketing Strategies Market Segmentation Market Strategy Focus Target Market(s) Strategy Example Mass marketing Customer similarities Full market coverage Pepsi and Coca-Cola in global markets Multi-segment Marketing Unique customer Two or more characteristics segments Selling both sports cars and family sedans Niche marketing (single-segment) Unique product/ service features Cutting-edge, high-tech personal videophones Premium price markets One-to-one marketing Highly specialized Mass customization Custom homes, cars, (single-segment) needs and wants micro-markets tailored clothes NB: A traditional approach Interactive Marketing Media Interactive Marketing Media Direct mail Telemarketing E-mail Web sites Broadcast Print The Basics of Direct Mail Types of Direct Mail addressed mail unaddressed mail co-op envelope, including card decks Benefits of Direct Mail personal (if addressed) highly selective highly responsive excellent testing vehicle most flexible of DM media Disadvantages of Direct Mail relatively expensive requires long lead times exacting technique with many pitfalls for the unwary Relative Value of Components Creative 25.0% List 40.0% Offer 35.0% The Basics of Telemarketing Definition of Telemarketing a systematic, targeted and professional medium used to generate a measurable response Types of Telemarketing Inbound 800/900 numbers Outbound proactive sales and/or follow-up Applications of Telemarketing Inbound fulfil literature requests sales lead generation dealer location order taking promotional messages market research Key Characteristics - reactive, 24x7 service, consumer/business Applications of Telemarketing Outbound direct mail follow-up credit card marketing market surveys marginal account management lead qualification database maintenance etc Do's and Don'ts Do's plan test involve ALL appropriate departments train TSR's develop reports Dont's expect immediate paybacks take shortcuts 'wing it' without a script forget to test Kobs’ 7 Principles* Know the target audience Get off on the right foot Develop “natural tone” copy Encourage dialogue Anticipate questions/objections Close, close, close Don’t wear out your welcome *Contemporary Direct Marketing, Spiller and Baier, pg. 181 The Basics of e-mail Pros and Cons Pros Speed Flexibility Low Cost Cons Viewed as SPAM Service provider filters Intrusive E-mail Considerations* Must examine, measure and test: ‘from line’ Subject line Filtering Day/time of delivery *From 24.7 Canada CMA Handouts, May 2004 E-mail Metrics* Successful events Open rates Click through rates Opt-out rates *From 24.7 Canada CMA Handouts, May 2004 The Basics of Internet Marketing* *this section from Contemporary Direct Marketing, Spiller and Baier, Paerson, 2005 Internet Evolution brochureware customer interactivity transaction enabler one-to-one relationship real-time organizations communities of interest (COINs) Pros and Cons Pros wide reach convenient selective low cost creative interactive flexible Cons limited reach privacy security ethical issues no tech support • consumer control Web Metrics hits pages visits users identified users navigation path Web Goal A sticky site to enable a “mutually beneficial exchange”