* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download strategic selling era
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Value proposition wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
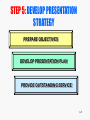
9TH EDITION Manning and Reece CHAPTER 1 PERSONAL SELLING AND THE MARKETING CONCEPT PART I 1-1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe contributions of personal selling to information economy Define personal selling—discuss as extension of marketing concept Describe evolution of consulting selling Define strategic selling and name four strategic areas of selling model Describe evolution of partnering—discuss how it relates to quality improvement Explain how value-added strategies enhance personal selling 1-2 CHANGES IN SELLING WORLDWIDE Scope of competitive selling environment Necessary skills to sell intangibles Adjustment to information age 1-3 PERSONAL SELLING IN INFORMATION AGE Evolution from industrial to information economy INDUSTRIAL--1950s INFORMATION--PRESENT See Table 1-1. 1-4 EVOLUTION OF PERSONAL SELLING MARKETING ERA 1950s CONSULTATIVE SELLING ERA 1960s-1970s STRATEGIC SELLING ERA 1980s PARTNERING ERA 1990s-Present 1-5 SHIFT TO INFORMATION ECONOMY INDUSTRIAL Advances in transport and manufacturing Strategic resources are capital and natural resources Products and factories define the business Sales success means meeting quotas INFORMATION Advances in information technology Strategic resource is information Business defined by customer relations Sales success depends on adding value 1-6 SELLING MODEL –STEP 1 Figure 1.2 1-7 PERSONAL SELLING: DEFINITION PERSON-TO-PERSON COMMUNICATION WITH PROSPECT – – – – – DEVELOPING RELATIONSHIPS DISCOVERING NEEDS MATCHING PRODUCTS WITH NEEDS COMMUNICATION OF BENEFITS A PROCESS THAT ADDS VALUE 1-8 BROAD CONCEPT OF PRODUCT INCLUDES: ISSUES INFORMATION IDEAS SERVICES AS WELL AS “HARD GOODS” EVEN TV NETWORKS REFER TO THEIR SHOWS AS “PRODUCT” 1-9 DEVELOP PERSONAL SELLING PHILOSOPHY ADOPT MARKETING CONCEPT VALUE PERSONAL SELLING BE PROBLEM SOLVER/PARTNER See Slide 15 for context. 1-10 PERSONAL SELLING EXTENSION OF MARKETING CONCEPT MOVING FROM PRODUCT TO CUSTOMER ORIENTATION 1-11 MARKETING’S FOUR P’s-MIX PRODUCT PLACE PRICE PROMOTION 1-12 MARKETING AND CONSULTATIVE ERAS MARKETING – Sales team as source of strategic information on…product--market-service CONSULTATIVE – Emphasis on need identification – Transactional selling – Information sharing & negotiation replace manipulation See Table 1-1 1-13 STRATEGIC AND PARTNERING ERAS STRATEGIC – Emphasis on strategic market plan – Tactics to achieve strategic plan – Product positioning vital PARTNERING – Customer, not product, as driving force – Emphasis on strategies that create customer value See Table 1-1 1-14 A STRATEGIC MARKET PLAN Outlines necessary methods and resources Considers areas to be coordinated Production Finance Marketing Personnel Influences the sale of products Serves as guide for strategic selling plan 1-15 STRATEGY AND TACTICS STRATEGY: Carefully conceived plan required to meet sales objectives TACTICS: Specific techniques, practices, and methods used in customer interaction 1-16 APPLICATION WHICH IS THE STRATEGY? WHICH IS THE TACTIC? – Use a fact sheet comparing wondercell with all other batteries TACTIC – Analyze features of all leading alkaline batteries STRATEGY 1-17 SELLING MODEL Figure 1.5 1-18 STEP 1 : DEVELOP PERSONAL SELLING PHILOSOPHY ADOPT MARKETING CONCEPT VALUE PERSONAL SELLING BE PROBLEM SOLVER/PARTNER 1-19 STEP 2: DEVELOP RELATIONSHIP STRATEGY ADOPT WIN-WIN APPROACH PROJECT PROFESSIONAL IMAGE MAINTAIN HIGH ETHICAL STANDARDS 1-20 STEP 3: DEVELOP PRODUCT STRATEGY BECOME PRODUCT EXPERT SELL BENEFITS, NOT FEATURES CONFIGURE VALUE-ADDED SOLUTIONS 1-21 STEP 4: DEVELOP CUSTOMER STRATEGY UNDERSTAND BUYER BEHAVIOR DISCOVER CUSTOMER NEEDS DEVELOP PROSPECT BASE 1-22 STEP 5: DEVELOP PRESENTATION STRATEGY PREPARE OBJECTIVES DEVELOP PRESENTATION PLAN PROVIDE OUTSTANDING SERVICE 1-23 INTERRELATIONSHIP OF BASIC STRATEGIES Figure 1.7 1-24 E-COMMERCE AND COMPLEX SALE Complex sales involve several forms of information technology support Tools include: – – – – electronic product catalogs contact management systems Internet applications presentation packages like this one See Chapters 5, 11, 15 for info tech applications. 1-25 EVOLUTION OF PARTNERING Buzzword of 1990s, business reality in 2000s “Strategically developed long-term relationship that solves customer’s problems” Relationship selling relies on customized approach to each client Enhanced with high ethical standards and sales automation 1-26 CUSHMANN WAKEFIELD 1-27 STRATEGIC ALLIANCES Goal: to gain advantage by teaming with other company Can you cite some current examples of strategic alliances? Need to build key win-win situation 1-28 VALUE CREATION Value = creative improvements enhancing customer experience Consumer economy rewards sales people who add value at each step When customer not aware of value added by salespeople, focus may shift to price Last slide Chapter 1. 1-29