* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
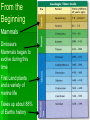
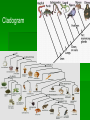
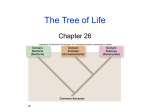
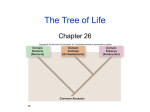
Evolution From the Beginning Mammals Dinosaurs Mammals began to evolve during this time First Land plants and a variety of marine life Takes up about 88% of Earths history Precambrian Time Is the longest time period Prokaryotes were first Anaerobic forms of life Ex. bacteria , these are things that don’t use oxygen Later photosynthetic forms of life appeared. Which added oxygen to the atmosphere. Aerobic, oxygen using, forms of life evolved and eukaryotes appeared Paleozoic Era Early in the Paleozoic Era there was a diversity of marine life Many invertebrate animals, with hard shells, also things such as jellyfish, worms, and sponges. Things with out a exoskeleton. Ancestors of squids and octopuses appeared along with aquatic arthropod First vertebrates appeared. First land plants appeared During this time period vertebrates began to invade the land. Reptiles, amphibians, winged insects, appeared At the end of this era there was a mass extinction affecting both plants and animals on land and in the sea Killing off as much as 95% of the complex life in the ocean Did not affect many fish and many reptiles also survived Mesozoic Era Events that occurred include the increasing dominance of dinosaurs. Flowering plants appeared Birds and flying reptiles Mammals evolved Leafy tree shrubs At the end there was a mass extinction killing off half of all the plant and animal groups and all of the dinosaurs Cenozoic Era Because of the extinction of the dinosaurs it gave way for mammals in the Cenozoic Era to take over. They took over on the land, water, and the air. Whales and dolphins evolved; so did grazing animals So did grasses and flowering plants During this period there were a series of ice ages. This is the time period humans evolved Fossil Record Relative Dating – dating a fossil by its relative placement in the rock bed Radioactive/Carbon Dating – uses the half life of radioactive isotopes to find out how old the fossil is How is a fossil formed- sediment settles on the dead organism and with time and pressure the remains become fossilized ( rocks) Pattern of Evolution Adaptive radiation - things evolve from a common ancestor Convergent evolution - having similar characteristics but are not from the same ancestor Ex. Sharks, dolphins Coevolution - When two species evolve in response to changes in each other over time Ex. Flowers and pollinators Punctuated equilibrium -long stable periods interrupted by brief periods of rapid change Gradualism -the gradual change from on species to another with intermediate species Adaptive radiation Convergent evolution Coevolution Darwin Voyage of the Beagle 1831- Darwin went to the Galapagos Islands . Darwin observed that the characteristics of many animals and plants varied noticeably among the different islands Evolution is the change in a species over time, the process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. Artificial selection- nature provides the variation and humans select those variations that they have found useful Struggle for existence- members of each species compete regularly to obtain food, living space, and other necessities of life Fitness-ability of an individual to survive and reproduce in its specific environment Adaptation- inherited characteristic that increase an organism’s chance of survival Natural Selection (survival of the fittest)these things are selected for or chosen for. Things survive based on how fit they are . Cannot be seen directly, only observed as changes in a population over time Over time, natural selection results in changes in the inherited characteristics of a population. These changes increase a species’ fitness in its environment. Descent with modification- over time, natural selection produces organisms that have different structures, niches, or occupy different habit Jean- Baptiste Lamarck- Inheritance of acquired traits. Means that what traits your parents acquired while alive they can pass on to you. Structures Vestigial- features or structures that have no use but seem to be left over from some evolutionary change. Ex. Wisdom teeth, Whales pelvis Homologues- They are common characteristics between like species. Ex. Bone structure of a human arm and frog arm Selection Directional- moves the population to one side or the other Stabilizing- moves it back to the middle Disruptive- moves it to the extremes Genetic Drift Genetic Drift Founders Effect- the original founders are the base of the gene pool Bottleneck- after the population has been dramatically killed off it lowers the gene pool Hardy-Weinberg Principle Genetic equilibrium- allele frequencies remain constant 5 conditions for Hardy-Weinberg Random Mating Large Population No movement into or out of the population (immigration, emigration) No mutation No natural selection Speciation Speciation- the formation of a new species What is a species? It is a group of organisms that breed with one another and produce fertile offspring This means that individuals in a species share the same gene pool Gene pool- is all the genes, including all the different alleles, that are present in the population What causes Speciation? Selection- mainly disruptive Isolation Mechanisms Reproductive isolation-When the members of two populations cannot interbreed and produce fertile offspring Behavioral isolation- this occurs when two populations are capable of interbreeding but have different courtship rituals Geographic isolation- live in different places, separated by geographical barriers Temporal isolation- reproduce at different times Classification What is classification? The naming or the putting things into groups based off of specific criteria Why do we classify things? Helps us to distinguish between things. The original classification was a description of the organism. Classification Naming order-Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species 3 Domains- Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya 5 Kingdoms- Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plant, Animal Phylum- there are 36 of these Ex. Chordata, Annelide, Arthopoda, Taxonomy- is the practice and science of classification Binomial Nomenclature-Carolus Linnaeus came up with this in the mid 1700s. It is a two name system to classify, group, things into. This is the one still used today. Human Scientific name Domain- Eukarya- multicellular, Kingdom- Animala- no cell wall Phylum- Chordata- has a back bone Class- Mammalia- has hair, mammary glands Order- PrimataFamily-HominidaeGenus- Homo Species- Sapiens Evolutionary Classification Phylogeny- the study of evolutionary relationships among organisms Evolutionary classification- it’s the strategy of grouping organisms together based on their evolutionary history Cladogram- a diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms. Phylogeny Cladogram Domain Archaea Unicellular Prokaryotic Cell Wall Both Autotrophic and Heterotrophic Most cannot live in oxygen Live in the extreme areas of the world Kingdom Archaebacteria Domain Bacteria Unicellular Prokaryotic Thick Rigid Cell Wall Both Autotrophic and Heterotrophic Both Photosynthetic and Aerobic Kingdom Eubacteria the larger of the 2 domains Domain Eukarya Eukaryote Cell- Have a nucleus Kingdoms Protista- Greatest variety, most are unicellular but some are multicellular, are both heterotrophic and autotrophic (everything that doesn’t fit into the other 3 kingdoms goes here)(Ex. Red, Brown & Green Algae) Fungi- Heterotrophic, feed on dead and decomposing organisms, they secrete digestive enzymes into their food source, (Ex. Mushrooms, multicellular; yeast, unicellular) Plantae- multicellular, photosynthetic autotrophs, nonmotile, cell wall, Animalia- multicellular, heterotrophic, no cell wall, movable,