* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution
Rotating locomotion in living systems wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Acquired characteristic wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Spontaneous generation wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
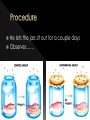
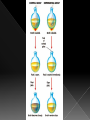
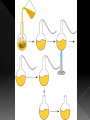
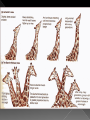
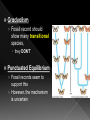
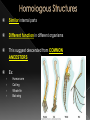
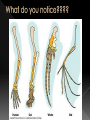
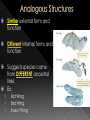
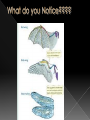
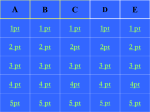
BIG IDEA: THE ENVIRONMENT SELECTS THE TRAITS OF ITS INHABITANTS. Biogenesis: › All living things come from other living things Spontaneous Generation : › States that life can come from nonliving matter Evolution : › the development of new types of organisms from preexisting organisms over time Natural Selection: › Is the mechanism for “descent with modification” Adaption: › A trait that makes an organism successful in its environment EX: thicker fur coats in cold climates Fitness: › Is a measure of an individual’s hereditary contribution to the next generation Homologous Structure: › structures that occur in different species and originate from a common ancestor Analogous Structure: › Structures that are closely related but do not derive from the same ancestor Vestigial Structure: › Structures that serve no function but that resemble structures with functional roles Fossil: › Are the remains of an organism that died long ago › EX: Dinosaur bones Control Group: › the group that doesn’t change Experimental Group › the group that has the variable A theory summarizes many hypotheses that have been supported It is accepted as long as there is NO evidence to disagrees with it So › They can be disproven 15 billion years ago › HUGE explosion that started the expansion of the universe This explosion BIG BANG!!!! It is thought that the explosion was more inward It laid for the foundation of the universe A piece of meat was left out. The next day flies and maggots were seen on the meat. Where did the flies come from? › The thought the meat. Is the idea that life can arise from nonliving matter. There is a “life force” Francesco Redi Lazzaro Spallanzani Louis Pasteur 1668 › Francesco Redi One scientist that performed an experiment that disproved spontaneous generation Control group: › Put meat in a jar uncovered. Experimental group: › Put meat in a jar covered. He lets the jars sit out for a couple days Observes…… Control Group: Flies found on the meat. Experimental Group: No flies on the meat. Conclusion › Flies do not come from the meat. Italian scientist 1768 › Performed another experiment that disprove spontaneous generation Control Group: › Boil broth › Left flask open Experimental Group: › Boil broth › Sealed flask Control Group: Experimental Group: Control: › Broth becomes cloudy bacteria present Experimental: › Broth remains clear NO bacteria The bacteria came from the air French chemist He disproved spontaneous generation Invented the Pasteurization method 1862: Boil broth in a curved-neck flask. › Curved-neck trapped large particles from getting into the body of the flask. Control › The neck on the flask was not broken Experimental › The neck on the flask was broken After a year, › Broth in the not broken neck of flask clear › Broth in the broken neck of flask cloudy Bacteria came from the outside air. All living things come from the reproduction of other living things. It is the idea that new organisms come from preexisting types of organisms. Jean Baptiste Lamarck Charles Darwin French Biologist Famous for his evolutionary theory of inheritance 1809 Two Theories 1. Use and Disuse 2. Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics Body parts that are used more grow stronger and bigger USE Body parts that are NOT used deteriorate DISUSE Physical changed that occur in an organism are inherited by their offspring(s). Giraffe’s neck › They gets longer as it stretches to reach food in trees. NO!!!!!! Variations that occur in the: › GAMETES cells are passed to offspring › SOMATIC (body) cells are NOT inherited British Naturalist Set sail on the HMS Beagle Famous for his studies with finches on the Galapagos Islands “Father of Evolution” Went to the Galapagos Islands He observed different types of finches These observation lead to him developing his theory of evolution British Naturalist Co discover of natural selection Wallace and Darwin presented their ideas to the public › Darwinism States: 1. Descent with modification 2. Evolution occurs by the process of natural selection. Decent of Modification Evolution Natural Selection Variation Adaptions “Survival of the Fittest” Fitness Speciation Specie states evolution is the development of new organisms from preexisting organisms over time. Over production: › In a population, more offspring are produced than can survive. Competition › Only some survive long enough to reproduce. There is variation within a population these variations are inherited. traits that are favorable and improve the organism’s ability to function and reproduce. States that survivors pass on their variations. Therefore….. a larger proportion in the next generation will have those variations. is a measure of an individual’s genetic contribution to the next generation. Over time, small changes accumulate and populations change. a group of organisms that can mate and produce fertile offspring. Organisms constantly strive to improve themselves and become more advanced This effort causes the most used body structures to develop, › while unused structures waste away AKA Used/Disused Theory Once a structure is modified, › It is inherited by the organism’s offspring Think about the muscles used by a runner There is always a variation amongst a population. Many variations are inherited and passed on to offspring However, some are more favorable Improve organism’s survival in the environment More young are produced in each generation than can survive Organisms that survive and reproduce are those with favorable characteristics He came to the same conclusions as Darwin did American Evolutionist He came up with Punctuated Evolution › Which defies the known way of evolution’s pace species remain the same for extended periods of time › then small changes occur States that for long periods of time, the existing species didn’t change Equilibrium Then, in relatively short periods of time, there is an interruption in the equilibrium New species emerge. Evolution that occurs slowly and continuously throughout time Lamarck’s Theory Darwin’s Theory The environment changes Which creates a need for organisms to change Organisms development new features which are passed down to offspring Newly acquired traits somehow get passed down to offspring New species eventually evolves Variations are inherited Environment: › selects features survival › eliminates others Those traits which: › help survival tend to survive › Those organisms have more offspring Therefore…..New species 1. 2. 3. 4. Fossil Evidence Anatomy Embryology Molecular Evidence Fossils: › remains/trances of organisms that died long ago › They are often found in strata Strata layered rock If undisturbed, › › the lowest stratum is the oldest the highest stratum is the newest Relative Age: › is found by comparing ages of strata Absolute age › is found by using radiometric dating • Fossil record suggests that different species were present in the past than today. Gradualism › Fossil record should show many transitional species, they DON’T Punctuated Equilibrium › Fossil records seem to support this › However, the mechanism is uncertain studies the parts or structures of living things. Similar internal parts Different function in different organisms This suggest descended from COMMON ANCESTORS Ex: › › › › Human arm Cat leg Whale fin Bat wing Similar external form and function Different internal forms and function Suggests species came from DIFFERENT ancestral lines Ex: › › › Bat Wing Bird Wing Insect Wing Is the study of embryos as they develop Similarities of the development of embryos: › suggests that the species have a common ancestor Is when we analyze chemical similarities between organisms Ex: a. DNA Comparison b. Protein Comparison The more DNA is similar the CLOSER the relationship between the organims Amino acids › The building blocks of proteins Similarities of amino acids that make proteins suggest a relationship between organisms EX: › In proteins the difference between amino acids…… Humans vs. monkeys 1 difference Human vs. pigs 10 differences