* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Ellipsometry wikipedia , lookup
Confocal microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Super-resolution microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction topography wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Photomultiplier wikipedia , lookup
Silicon photonics wikipedia , lookup
Optical amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Photoacoustic effect wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Franck–Condon principle wikipedia , lookup
Phase-contrast X-ray imaging wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Resonance Raman spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Upconverting nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Gamma spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Vibrational analysis with scanning probe microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Chemical imaging wikipedia , lookup
Mössbauer spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Atomic absorption spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Johan Sebastiaan Ploem wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction grating wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
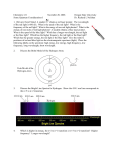
Instrumental Analysis: Spectrophotometric Methods 2007 By the end of this part of the course, you should be able to: •Understand interaction between light and matter (absorbance, excitation, emission, luminescence,fluorescence, phosphorescence) •Describe the main components of a spectrophotometer, (sources, monochromators, detectors, interferometer, grating, ATR, ICP, ) •Make calculations using Beer’s Law (analyse mixture absorption) •Understand the mechanism and application of UV-Vis, FTIR, Luminescence, atomic spectroscopy Background knowledge: What you are expected to know before the course: Error analysis in quantitative analysis Solve linear equations Complementary colour Exponential and logarithm If you have difficulty to understand above topics, find extra reading materials! Or discuss with me after the lecture. What you are recommended to know before the course: Least square fitting Basic quantum chemistry Molecular symmetry If you are trying to learn above topics, please let me know. Today’s lecture: (Instruments based on light interaction with matter) • • • • Properties of light Molecular electronic structures Interaction of photons with molecules Spectrophotometer components • Light sources • Single and double beam instruments • Monochrometers • Detectors Fluorescence spectroscopy • Next week’s lecture: • • • Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy • Interferometer Atomic spectroscopy Quantitative analysis • Beer’s law • Method validation • Dilution and spike Review on properties of light:photon Light is energy in the form of electromagenetic field Wavelength (l): Crest-to-crest distance between waves Frequency (n): Number of complete oscillations that the wave makes each second units: number of oscillations/sec or s-1 or Hertz |(Hz) Light travelling speed: in other media: c/n (n = refractive index, generally >1) in a vacuum: c=2.998 x 108 m s-1 (n=1 exactly, in air n=1.0002926) c/n= nl And of course, the relationship between energy and frequency: ~ E = hn = hc/l = hc n h = Planck’s constant (6.626 x 10-34 J s) n =~wavenumber (most common units = cm-1) Therefore: Energy is inversely proportional to wavelength but proportional to wavenumber Frequency Scanning Techniques: a few definitions Emission method: source of light is sample Absorption method: intensities of a source with and without the sample in place are compared Spectrum: a plot of intensity vs. frequency/wavelength In quantitative analysis: common to work at 1 wavelength running a spectrum is an important initial step (to select best conditions) Regions of Electromagnetic Spectrum-the “colour” of light Fig. 18-2 Energy Electronic structures of simple molecule Vibration states Excited state Singlet S1 T1 Excited state Triplet D Dissociated states S0 Ground state Bond length Interaction between photon and molecule S0 S1 transition S1 T1 UV-vis S1 T1 A D F P IR S0 S0 Key concept from energy diagram Electronic structures Singlet and triplet Bond length for ground and excited states Vibrational structures-infrared absorption/transmission (FTIR) Internal conversion Intersystem crossing Photon adsorption excitation (Beer’s law, UV-vis) Frank Condon condition and The Stokes' shift Radionless relaxation and vibration relaxation Luminescence-fluorescence/phosphorescence Type of optical spectroscopy UV-vis absorption spectroscopy (UV-Vis) FT-IR absorption/transmission spectroscopy (FTIR) Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS) X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XFS) What you will learn: The excitation mechanism Monochromator design Instrument principle Quantitative methods Optical spectrophotometer components Excitation sources Deuterium Lamp Tungsten Lamp Laser X-ray tube UV UV-vis X-ray, UV, vis, IR X-ray Mercury lamp UV-vis Xenon lamp UV-vis Silicon carbide globar Flame IR Detectors Monochromators Filters Grating+slit prism PMT CCD/CID Photodiode Thermocouple MCT Pyroelectric detector Furnaces Plasmas Hollow-cathode lamp What is the advantage and disadvantage? Design of optical spectrophotometers Single Beam vs. Double Beam Q: what’s the advantage of double beam spectrophotometer? (a) single-beam design (b) dual channel design with beams separated in space but simultaneous in time (c) double-beam design in which beams alternate between two channels." (a) (c) (b) Fig. 13-12, pg. 315 "Instrument designs for photometers and spectrophotometers” Light sources What is the important properties of a source? Brightness Line width Background Stability Lifetime Black-body radiation for vis and IR but not UV - a tungsten lamp is an excellent source of black-body radiation - operates at 3000 K ( How much in cm-1, J, Hz and eV?) - produces l from 320 to 2500 nm For UV: - a common lamp is a deuterium arc lamp - electric discharge causes D2 to dissociate and emit UV radiation (160 – 325 nm) - other good sources are: Xe (250 – 1000 nm) Hg (280 – 1400 nm) Lasers: - high power - very good for studying reactions - narrow line width - coherence - can fine-tune the desired wavelength (but choice of wavelength is limited) - £££ expensive £££ Sample a source containers: for UV: quartz (won’t block out the light) for vis: glass [l 800nm (red) to l 400 nm (violet)] for IR: NaCl (to or 15384 nm or 650 cm-1) KBr (to 22222 nm or 450 cm-1) CsI (to 50000 nm or 200 cm-1) Best material: diamond, why? Optical transmission coefficient Criteria High transmission Chemically inert Mechanically strong Monochromators Early spectrophotometers used prisms - quartz for UV Why? - glass for vis and IR These are now superseded by: Diffraction gratings: - made by drawing lines on a glass with a diamond stylus ca. 20 grooves mm-1 for far IR ca. 6000 mm-1 for UV/vis - can use plastic replicas in less expensive instruments Think of diffraction on a CD 10mmx10mm http://www.veeco.com/library/nanotheater_detail.php?type= application&id=331&app_id=34 http://www.ii.com/images/prism.jpg http://www.mrfiber.com/images/ cddiffract.jpg Monochromators: cont’d What is the purpose of concave mirrors? Polychromatic radiation enters The light is collimated the first concave mirror Reflection grating diffracts different wavelengths at different angles Second concave mirror focuses each wavelength at different point of focal plane Orientation of the reflection grating directs only one narrow band of wavelengths to exit slit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov/images/grating_spec-br.jpg Interference in diffraction d sin(q)+d sin(f)=nl d q>0 f<0 q Bragg condition f Phase relationship n=1, 2, 3 In-phase n=1/2, 3/2, 5/2 out-phase Monochromators: reflection grating Monochromators: reflection grating Each wavelength is diffracted off the grating at a different angle Angle of deviation of diffracted beam is wavelength dependent diffraction grating separates the incident beam into its constituent wavelengths components Groove dimensions and spacings are on the order of the wavelength in question In order for the emerging light to be of any use, the emerging light beams must be in phase with each other l Resolution of grating: Dl Angular resolution: As: So: Therefore: =nN n: diffraction order N: number of illuminated groves d sin(q)+d sin(f)=nl n Dl=d cos(f) Df Df/Dl=n/[d cos(f)] What does this mean? Monochromators: slit Bottom line: - it is usually possible to arrange slits and mirrors so that the first order (n = 1) reflection is separated - a waveband of ca. 0.2 nm is obtainable However, the slit width determines the resolution and signal to noise ratio Large slit width: more energy reaching the detector higher signal:noise Small slit width: less energy reaching the detector BUT better resolution! Detectors : Radiation-----charger converter Choice of detector depends upon what wavelength you are studying Want the best response for the wavelength (or wavelength range) that you are studying In a single-beam spectrophotometer, the 100% transmittance control must be adjusted each time the wavelength is changed In a double-beam spectrophotometer, this is done for you! Photomultiplier-single channel, but very high sensitivity - Light falls on a photosensitive alloy (Cs3Sb, K2CsSb, Na2KSb) - Electrons from surface are accelerated towards secondary electrodes called dynodes and gain enough energy to remove further electrons (typically 4-12, to 50 with GaP). - For 9 stages giving 4 electrons for 1, the amplification is 49 or 2.6 x 105) - The output is fed to an amplifier which generates a signal - To minimise noise it is necessary to operate at the lowest possible voltage What decide the sensitive wavelength? Photodiode Array-multiplex, but low sensitivity Good for quick (fraction of a second) scanning of a full spectrum Uses semiconductor material: Remember: n-type silicon has a conduction electron – P or As doped p-type silicon has a ‘hole’ or electron vacancy – Al or B doped A diode is a pn junction: under forward bias, current flows from n-Si to p-Si under reverse bias, no current flows boundary is called a depletion layer or region Photodiode Array - Electrons excited by light partially discharge the condenser - Current which is necessary to restore the charge can be detected - The more radiation that strikes, the less charge remains - Less sensitive than photomultipliers several placed on placed on single crystal - Different wavelengths can be directed to different diodes - Good for 500 to 1100 nm - For some crystals (i.e. HgCdTe) the response time is about 50 ns Could you compare photodiode with CCD detector? Photodiode Array Spectrophotometer - For photodiode array spectrophotometers, a white light passes through sample - The grating polychromator disperses the light into the component wavelengths - All wavelengths are measured simultaneously - Resolution depends upon the distance between the diodes and amount of dispersion No moving parts! Simple mechanical and optical design, very compact. Photodiode Array Spectrophotometers vs Dispersive Spectrophotometers Dispersive Spectrophotometer: - only a narrow band of wavelengths reaches the detector at a time - slow spectral acquisition (ca. 1 min) - several moving parts (gratings, filters, mirrors, etc.) - resolution: ca. 0.1 nm - produces less stray light greater dynamic range for measuring high absorbance - sensitive to stray light from outside sources i.e. room light Photodiode Array Spectrophotometer: - no moving parts rugged - faster spectral acquisition (ca. 1 sec) - not dramatically affect by room light What are the components 1 to 10? From: http://www.oceanoptics.com/ Property of luminescence spectrum Fluorescence vs phosphorescence 1. Phosphorescence is always at longer wavelength compared with fluorescence 2. Phosphorescence is narrower compared with fluorescence 3. Phosphorescence is weaker compared with fluorescence Why? Absorption vs emission 1. absorption is mirrored relative to emission 2. Absorption is always on the shorter wavelength compared to emission 3. Absorption vibrational progression reflects vibrational level in the electronic excited states, while the emission vibrational progression reflects vibrational level in the electronic ground states 4. l0 transition of absorption is not overlap with the l0 of emission Why? Fluorescence spectroscopy Fluorescence spectroscopy Beam splitter Light source Excitation monochromator sample Q: why the emission is measured at 90 relative to the excitation? Emission Monochromator Reference diode PMT Amplifier Computer Emission spectrum: hold the excitation wavelength steady and measure the emission at various wavelengths Excitation spectrum: vary the excitation wavelength and vary the wavelength measured for the emitted light Fluorescence spectroscopy: well defined molecules Summary of spectrophotometric techniques • • • Describe the main components of a spectrophotometer and distinguish between single double beam instruments Describe suitable sources for ultraviolet (UV)/visible (vis), infra red (IR) and atomic absorption (AA) instruments • Describe and assess advantages and disadvantages of various monochromators e.g. Prism, diffraction gratings Explain how to asses the quality of grating • • • • Explain how photomultipliers and diode detectors work Explain the advantage of multiplex detecting Describe the luminescence spectroscopy and energy transfer process Compare the emission and absorption spectrum