* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab 3 - Geologic Structures, Maps, and Block Diagrams
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Map projection wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Seismic communication wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Diver navigation wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Surface wave inversion wikipedia , lookup
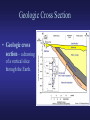
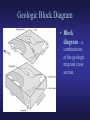
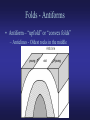
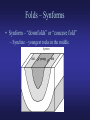
Lab 3 – Structural Geology and Earthquakes Definitions • Structural Geology – study of how geologic units (bodies of rock or sediment) are arranged when first formed and how they are deformed afterward. Geologic Map • Geologic map – shows the distribution of rocks at the Earth’s surface. – Formations – mappable rock units • Beds – subdivisions of formations • Example: Cretaceous Kootenai = sandstone formation, Gastropod Limestone = bed within Kootenai – Contacts – boundaries between geologic units Geologic Cross Section • Geologic cross section – a drawing of a vertical slice through the Earth. Geologic Block Diagram • Block diagram – a combinations of the geologic map and cross section. Strike and Dip • Attitude – the orientation of a rock unit or surface. – Strike – the compass bearing (direction) of a line formed by the intersection of a horizontal plane and an inclined layer (bed/stratum) of rock, fault, or fracture. – Dip – the angle between a horizontal plane and the inclined (tilted) stratum, fault, or fracture. • Dip direction – perpendicular to the line of strike, direction in which water will run downhill. • Dip angle – inclination of dip down from the horizontal line. Unconformities • Disconformity – an unconformity between parallel strata. • Angular unconformity – an unconformity between nonparallel strata. • Nonconformity – an unconformity between sedimentary rock/sediment and non-sedimentary (ign./met.) rock. Faults • Types: normal, reverse (high angle), thrust (low angle), transverse (strike-slip) • Remember: – – – – Stress fields Angles Hanging wall Foot wall Folds - Antiforms • Antiform – “upfold” or “convex folds” – Anticlines - Oldest rocks in the middle young old young Folds – Synforms • Synform – “downfolds” or “concave fold” – Syncline – youngest rocks in the middle old young old Other types of folds Basins Domes Earthquakes • Earthquakes – shaking motions and vibration caused by release of energy in the Earth. • Epicenter – point on Earth surface directly above the focus (origin of earthquake) • Seismic waves – elastic waves of vibration and shaking cause by stain. – P-waves – primary waves, compressional – S-waves – secondary waves, shear – Rayleigh/Love waves –move along Earth’s surface • Seismograph – instrument to record seismic waves • Seismogram – record of seismic waves Earthquake Damage • Damage related to: – – – – Energy Amplitude Soil strength Building strength • Unconsolidated sediment amplifies waves. Earthquake location