* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Changing Environment - Mr. Hamilton`s Classroom
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Meteorology wikipedia , lookup
Tunnel valley wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Ice-sheet dynamics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Quaternary glaciation wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
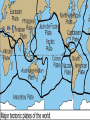
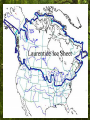
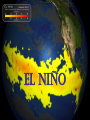
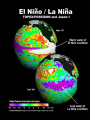
Chapter 3 Section 1: The Changing Environment Structure of an Ecosystem In addition to abiotic factors, a(an) ECOSYSTEM includes COMMUNITIES Made up of Different POPULATIONS Of organisms that are Members of different SPECIES OBJECTIVE Describe the ways in which the layers of the biosphere change over time. Vocabulary • Tectonic Plates • Weathering • Erosion Introduction • Earth is approximately 4.6 billion years old • Humans have existed for about 100,000 years • Many rapid changes have taken place due to results of human activity Changes in the Lithosphere How are land formations created? Movement of the tectonic plates Weathering Erosion Tectonic Plates Several large, movable plates that make up the lithosphere. Tectonic Plates Weathering The breaking down of rocks by weather and water. Weathering Weathering Weathering Erosion The wearing away of land by weather and water; a natural process where soil is lost, transported, and reformed. Erosion Changes In The Hydrosphere ICE AGES EL NIÑO An Ice Age is a long period of cooling during which huge ice masses, called glaciers, grow and extend from Earth’s polar regions, covering much of the planet’s surface. Ice Ages Ice Ages • During the ice age, sea levels lower. • As glaciers melt, sea levels rise. • After an ice age, the glaciers melt and shrink back toward the poles. • Most recent ice age ended between 10,000 and 12,000 years ago. Significant changes due to glaciers • Changes the shape of the land • Scraping of ice across the land • Displacement of rocks • Large scale weathering and erosion • Deposit of foreign minerals EL NIÑO EL NIÑO • A current of warm, nutrient-poor water that flows southward along the coast of South America. Occurs every year near the end of December • Normally last for a couple weeks. • When this current lasts for several months, the condition is called El Niño. EL NIÑO • One of many recurring patterns of change in the ocean. • Change in water temperature and nutrient content affects the survival of fish. • Drop in fish means loss of income for the fishing industry. • Reduced supply of fish also means increased costs for other industries that depend on fish meal, such as poultry and egg farming. • Climatic changes also damage crops. CHANGES IN THE ATMOSPHERE Background Information • Sunlight and Earth’s rotation drive many of the daily and seasonal changes in the atmosphere. • Before life on Earth, erupting volcanoes was the source for Earth’s atmosphere. • Organisms evolved and were able to combine water, carbon dioxide, and energy from the sun to produce food (Photosynthesis). • This process released the first Oxygen (O2) into the atmosphere. Erupting Volcanoes http://dsc.discovery.com/videos/volcanovideo/ Greenhouse Effect • The trapping of radiated heat by gases in the atmosphere. • One way in which humans may be changing Earth’s atmosphere. • Loss of ozone (O3) from the stratosphere and increased pollution in the troposphere are other examples of atmospheric changes caused by humans. SECTION 3.1 REVIEW Question #1: Through what process does weather affect the shape of land? Answer: Weather affects the shape of the land through erosion. Question #2: In what ways does El Niño affect the economy? Answer: By affecting climate and water quality, farming and fishing industries are affected. Question #3: Describe how ice ages are related to changes in the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. Answer: In age ices, the state of water changes in the hydrosphere, air bubbles are trapped, and land is eroded in the lithosphere.