* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download geography2
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Overdeepening wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
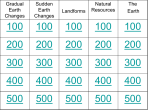
Chapter 2-1 Shapes on the Earth’s surface landforms The shape, height, and arrangement Of landforms in a particular place. Topography Describes how Earth’s surface is formed and how it changes. plate tectonics Mountain ranges are formed when tectonic plates collide When two plates move apart, what may Be created by the emerging hot lava? Mountain ranges Melted rock from deep in the Earth lava Earth’s plates can shift in which ways? sliding, moving apart, and colliding. Weathering is caused by chemicals in plants, freezes and thaws, and water dissolving minerals. The process of breaking down rock by wind, water, and ice weathering The most influential force in the erosion and shaping of land is flowing water Large, slow rivers of ice that can move tons of rock glaciers On steep hillsides, farmers often create horizontal ridges like steps, called tarraces