* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1: Basics of Geography Chapter 2
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
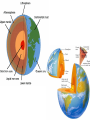
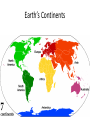
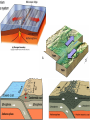
Unit 1: Basics of Geography Chapter 2: A Living Planet Chapter 2, Section 1: The Earth Inside and Out Earth’s Structure • Inside Earth: – Core: center, iron and nickel • Inside = solid; outside = liquid – Mantle: outside of the core, has multiple layers and contains most of the earth’s mass • Magma: molten rock – Crust: thin layer of rock at earth’s surface Earth’s Structure • On and Above Earth: – Atmosphere: layer of gases surrounding the earth – Lithosphere: solid rock portion of the earth’s surface • uppermost mantle and crust • Seafloor – Hydrosphere: all the oceans, seas, rivers, lake, and water in the atmosphere – Biosphere: part of earth where plants and animals live. Earth’s Continents How Has the Earth Changed? • Continental Drift – Alfred Wegener (1912) – Earth was once a supercontinent that divided and drifted apart over millions of years Chapter 2, Section 2: Bodies of Water and Landforms Bodies of Water • Hydrologic cycle- continuous circulation of water between atmosphere, oceans, and earth. Bodies of Water • Lakes, rivers, streams – Drainage basin-area drained by a major river and its tributaries – Ground water-water held in pores of rock – Water table- level at which the rock is saturated • Rise or fall depending on amount of precipitation in the region Landforms • Naturally formed features on the surface of the earth – Examples??? Landforms • Oceanic – Continental shelf- edge of a continent to the deep part of the ocean • Ridges, valleys, canyons, plains, mountain ranges Chapter 2, Section 3 & 4: Forces Shaping the Earth Plate Tectonics • Enormous moving pieces of the earth’s lithosphere Plate Tectonics • Divergent boundary-plates move apart, spreading horizontally • Convergent boundary- plates collide, causing either one to dive under the other or the edges of both to crumple • Transform boundary- plates slide past one another Earthquakes • As plates grind past at a fault, earthquakes happen. – Measure using seismograph – Richter Scale: determines strength • The point directly above the focus of the earthquake is the epicenter Tsunami • Caused by earthquakes, giant wave in the ocean • 50-100 feet tall Volcanoes • Magma, gasses, water from lower part of the crust collect in underground chambers • Magma pours out of a crack in the earth’s surface – Lava Weathering • Physical and chemical processes that change the characteristics of rock – Breaks down rocks into smaller pieces: sediment • Mud, silt, sand • Mechanical Weathering – Physical, does not change the composition of the rock, just the size • Chemical Weathering – Rock is changed into a new substance due to reactions w/ elements in air or water Erosion • Weathered material is moved by wind, water, ice, gravity Building Soil • Loose mixture of weathered rock, organic matter, air, and water that supports plant growth • Soil factors: – Parent material – Relief – Organisms – Climate – Time