* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Structure
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
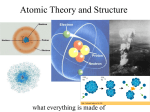
Atomic Structure What is an atom ? Element : Aluminium (Al) An Atom of Aluminium Atoms of Aluminium What is an atom ? •smallest particle of any substance •average diameter is approx. 10-10 m (analogy : 1016 atoms needed to cover a full stop) •each atom is made up of even smaller sub-atomic part •atoms differ from each other due to the different combinations of these sub-atomic particles Atoms of different elements differ in size and mass. Trends in Discovery of structure of atom Source : CD-ROM Chemistry Concepts and Applications by Glencoe Structure of an Atom nucleus shell electrons protons and neutrons Structure of Helium atom 2 protons 2 neutrons 2 electrons Source : Intro to Chemistry by Cyber Ed Inc. Sub-atomic particles particle proton neutron zero electron -1 charge +1 mass 1 1 1/1850 location In nucleus In nucleus In shells around nucleus Mass number; Atomic Number Mass number (or nucleon number)-the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom Nucleon = protons + neutrons Atomic number (or proton number) - the number of protons in an atom The atomic number is fixed for each atom. An atom is identified by its atomic number. Different elements have different atomic number. Proton and Mass Numbers The data are available in the Periodic Table : E.g. Mass number 23 11 Proton number Na Proton (Atomic) Number The proton (atomic) number of an element is the number of protons in its atom. E.g. Since the proton number of sodium is 11, it means that •every sodium atom has 11 protons. •Conversely, any atom with 11 protons is a sodium atom. Mass (Nucleon) Number The mass (nucleon) number refers to the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Hence, number of neutrons in an atom = mass number - proton number Example Derive the number of protons, electrons and neutrons in a sodium atom 23 11 Mass number = 23 Na Atomic number = 11 Number of protons = 11 Number of electrons = 11 Number of neutrons = 23 - 11 = 12 A short Quiz……. Malaysium (Ma), an imaginary element contains 111 protons and 141 neutrons. How would you represent the atom of Malaysium in symbolic form? Atomic number = Number of protons = 111 Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons = 111 + 141 = 252 Hence 252 111 Ma Isotopes Definition : Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons; Isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. Isotopes Isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. Isotopes 23 11 Na 24 11 Na number of protons 11 11 number of electrons 11 11 number of neutrons 23 - 11 = 12 24 – 11 = 13 Arrangement of electrons in the atom Electrons are arranged in energy levels (called electron shells) around the nucleus. The nearer the shell to the nucleus, the lower the energy level. Each energy level can hold a certain number of electrons. For the first 20 elements in the Periodic Table, 1st shell : 2 electrons 2nd shell : 8 electrons 3rd shell : 8 electrons To work out the arrangement of electrons Find out the proton number of the atom or element ; then for a neutral atom, the no. of electrons = the proton number (i) (i) Main rule -- electrons always go into the shell nearest to the nucleus ,if there is room. Once the shell is filled up, the electrons go into the next available shell and so on. Eg. electronic structure of Al - - - - - + - - - - Valence electrons Outermost shell OR Valence shell - shell outermost from the nucleus Valence electrons (Outermost electrons) electrons in the outermost shell determines the chemical properties of an element Electron Arrangement & the Periodic Table The position of an element in the Periodic Table is determined by its proton number. All elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, which is the same as the Group number. All elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells. Electron Arrangement & the Periodic Table Elements in : (a)the same Group same number of outermost / valency electrons (b)the same Period same number of electron shells electronic structures and the Periodic Table the Periodic Table VIII group number proton number name of element symbol full electronic structure simplified electronic structure I II III IV V VI VII