* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download c/catt-brams - EELA Documents
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
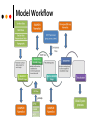
C/CATT-BRAMS description for EELA-2 Grid School Claudio Baeza Retamal Rodrigo Delgado Urzúa CMM/DIM, Universidad de Chile Chile The BRAMS Team CPTEC / INPE Brazil Agenda Introduction HPC for enviromental sciences @ CMM SAEMC Project What is C/CATT-BRAMS? Software Requirements Grid Requirements The GEL Introduction: who we are Center for Mathematical Modeling (CMM) is a center for research on applied mathematics Born at Department of Mathematical Engineering It belongs to Faculty of Science Physics and Mathematics of University of Chile In mathematics, Universidad de Chile is ranked 67th preceded only by the best from USA, Europe, 2 from China, 1 from Israel, 1 from Australia, 1 from Canada. U. de Chile + U. de Concepción = near 50% of Chilean Mathematics Strengths of the team: CMM’s numbers 2008 • • • • • • 32 researchers (24 U. de Chile, 8 U. de Concepción.) 4 CNRS researchers, as CMM is a CNRS’s UMI 28 researcher engineers & scientist 90 visitors: average 1month each 15 postdocs (mainly Europe, Latin America) 500+ published ISI papers from 2000- • • • • • 40 Ph.D. students 14 Ph.D. theses 70 Mathematical Engineering students 10 Engineering theses (Master level) 3500 undergraduate students (top 1% in the country) Goal at CMM: To establish meaningful and productive relationships between advanced mathematics and all endeavors of modern society Laboratories: bridge connecting basic and industrial research Fundamental Research Optimization Probability Nonlinear Analysis Discrete Math. Math. Mechanics Num. Analysis •LBMG •ESML •LM4 •GeoM Industry Mining Telecom. Energy Forestry •Forest •Econ •RR •SS •Education Fishing Biotechnology Environment Education HPC for Environmental Sciences @ CMM: ESML …Earth System Modeling tools and more particularly to provide a functional and validated basis on atmospheric chemistry and climate research... Collaboration with DMC (Chile), SMHI (Sweden), CPTEC (Brazil), NOAA (USA), INRIA/ENPC (France), among others. 7 HPC for Environmental Sciences @ CMM: ESML Emissions : mobile and stationary Adaptation (Porting) + Evaluation + Validation of models: MATCH, RCA MM5, WRF (CATT/CCATT)-BRAMS Polyphemus (POLAIR) 8 SAEMC Goals SAEMC (http://saemc.cmm.uchile.cl) project main goals: To provide accurate regional emissions and climate change scenarios for South America, with emphasis on the impacts of and on mega-cities. To establish the basis for operational chemical weather forecast for South American mega-cities. To strengthen and expand an active research and capacity building network in the Americas functional to Earth System Modeling. Multi-national partners: AR, BR, CL, CO, PE, US Strong emphasis on training human resources capable of making contributions in scientific and technical fields. 9 SAEMC + HPC WP1: Mobile and Stationary emissions scenarios estimate and evaluation WP2: Dynamical down-scaling of climate change scenarios WP3: Pilot implementation of chemical weather forecast network and tools for South American mega-cities WP4: Prospective characterization of aerosols in and downwind from South American mega-cities WP5: High Performance and Grid Computing for operational chemical weather forecast Researchers: Eugenio S. Almeida (CPTEC, Brazil), Claudio Baeza (CMM, Chile) , Rodrigo Delgado (CMM, Chile), Luiz Flavio Rodrigues (CPTEC,Brazil) 10 What is C/CATT-BRAMS? Coupled Atmospheric Tracer and Transport Chemestry Brazilian developments to Regional Atmospheric Modeling System What is C/CATT-BRAMS? BRAMS: multipurpose, numerical prediction model designed to simulate atmospheric circulations spanning in scale from hemispheric scales down to large eddy simulations (LES) of the planetary boundary layer. What is C/CATT-BRAMS? C/CATT-BRAMS explores the BRAMS tracer transport capability of using slots for scalars. The in-line model transport follows the Eulerian approach, solving the mass conservation equation for carbon monoxide (CO) and particulate material PM2.5 What is C/CATT-BRAMS? Software requirements C/C++ and Fortran compilers Gnu C Compiler Compiler (gcc/g++) / GNU Fortran Compilers (gfortan) Portland Group compiler suite 6 or later Intel C/C++ and Fortran compiler 9 or later For Intel 64 compatible CPUs, we recommend Intel compiler set. BRAMS MPI implementation on IA64 systems has been tested but is not suitable for production environments. Software requirements Regular libraries: HDF 4.2r0 or higher (not compatible with HDF 5) zLib 1.1.4 or higher jpeg-6b sZip 1.2 or higher Model Workflow Grid requirements Control of Job Failures Manage data and metadata Manage checkpoint Accounting Monitoring To keep a “know-how” along to databases on grid Know-how from EELA1 In EELA1 we adopted the strategy of to introduce system calls in source code for interact with the GRID. These system calls execute scripts (in Perl, Python, shell) or binary program (that uses gLite APIs) for connect the applications with Grid elements. Finally, we introduce the GEL concept The Grid Enabling Layer (GEL) A. S. Cofiño, M. Carrillo, C. Baeza, et al. “GRID distributed computation of nested climate simulations”, Geophysical Research Abstract, European Geosciences Union, Vol.9, 10351, 2007 V. Fernández-Quiruelas, J. Fernández, C. Baeza, et al. “Climate modeling on the GRID”, Third Conference of EELA Project, 2007 V. Fernández-Quiruelas, J. Fernández, A. Cofiño, C. Baeza, et al, “Complex Workflow Management of the CAM Global Climate Model on the GRID”, International Conference on Computational Science 2008 (ICCS 2008), Kraków, Poland V. Fernández-Quiruelas, J. Fernández, C. Baeza, A. S. Cofiño, J. M. Gutirrez. “Workflow management in the GRID, for sensitivity studies of global climate simulations”, Earth Science Informatics, Springer, Journal no. 12145 How to “gridify” our applications The main idea is to use the GEL layer for “gridify” the C/CATT-BRAMS application In EELA1 we use AMGA as metadata server, however, in the grid C/CATT-BRAMS applications, due to performance reasons, we prefer to develop another interface for metadata information, the amount of files is very big. The interface will be based on AMGA, but do not simulate a file system, simply, will use SQL instruction directly and protocols for synchronization and coordination, for example, a two phase commit. Thanks! Obrigado! Gracias!