* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
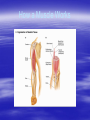
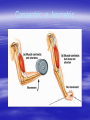
Training Effects on the Body The SAID Principle • Specific Adaptations to Imposed Demands • What does this mean? • How does this apply to training and sports? • Callous vs. Blister Overload Principle • Must overload the body part to make it adapt. • Rubbing body part on a smooth surface does not cause a blister or a callous • Lifting 1 lb will not increase strength • With Athletics we should be overloading right up to failure • As you get “stronger” you must continue to increase the overload Strength vs. Power • Strength - maximum force exerted o Distance running • Power – Maximum force exerted quickly o Sprinting How a Muscle Works Types of Muscle Contractions • Isometric • Isotonic o o Concentric Eccentric • Isokinetic • http://www.youtube.com/wa tch?v=wAKa5MCIKAY • http://www.youtube.com/wa tch?v=NsDl79yElK0 Isometric Contraction • “same” “distance” • No movement at the joint • Muscle does not shorten or lengthen • Minimal strength gains Isotonic Contraction • Change in muscle length • Concentric – Muscle shortens Traditional lifting technique • Eccentric – Muscle lengthens Negatives Greatest strength gains Concentric Exercise Eccentric Contractions Eccentric and Concentric Isokinetic Contractions • The limb is moved through a constant speed • Used in rehab • Gives good control of the limb • Measured in degrees per second Concentric vs. Isometric What happens to the muscles when you train them? • Hypertrophy – muscles gets bigger o We don’t get more muscle fibers but the ones we already have get bigger • Atrophy – muscles get smaller o Occurs when muscles are not used Post-op Stretching • Increases ROM at the joint • Tends to decrease injury • Can lead to better athletic performance • Dynamic/Ballistic before • Static after Types of Stretches • Types • Ballistic – bouncing. • Dynamic – Movement throughout ROM • Static – steady stretch • PNF -mixture of contractions and relaxations Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation Contract-Relax http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4GWlJMSAlu4 It is Important to avoid overstretching Predisposition to injury and possible nerve damage Warm-Up • Increase blood flow to working muscles • Increase temperature in working muscles • This increases the elasticity of soft tissue • Dynamic Stretching should be done after a proper warm-up • Static Stretching can predispose individuals to fatigue quicker than individuals who did not stretch