* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11 Supplement 2 Muscle Physiology
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Weight training wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac output wikipedia , lookup
Exercise physiology wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Human vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
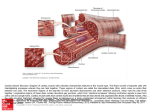
Chapter 11 Supplement 2 Muscle Physiology CARDIAC AND SMOOTH MUSCLE TISSUE PowerPoint by John McGill Supplemental Notes by Beth Wyatt CARDIAC MUSCLE TISSUE LOCATION MAJOR FUNCTION Located in the Wall of the Heart Pumps Blood (By Contraction) TYPE OF CONTROL Involuntary Cardiac Muscle STRUCTURAL FEATURES STRIATIONS Present (Striated) Means Sarcomeres Present NUCLEUS 1/Cell Cardiac Muscle STRUCTURAL FEATURES T TUBULES Present* SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM Present* * NOTE: Though Both Are Present, Their Arrangement Is Different Than in SMF’s (Less Extensive; Ca++ In From Outside the Cell) Cardiac Muscle SPECIAL FEATURES INTERCALATED DISCS Junctions That Tightly Join Cardiac Muscle Fibers Lengthwise BRANCHING Transverse Connections Between Fibers Cardiac Muscle METHOD OF CONTRACTION SYNCYTIUM Cardiac Muscle Tissue Contracts as a SYNCYTIUM (Unit of Combined Cells) Due To Special Features (Intercalated Discs & Branching)(Creates a Continuous Sarcolemma) Cardiac Muscle METHOD OF CONTRACTION SELF-EXCITING (myogenic) Cardiac Muscle Tissue is Self-Exciting Doesn't Need Stimulation by Nerve Impulses Stimulation Comes from Within the Tissue (Conduction System) SMOOTH MUSCLE TISSUE LOCATION Located in the Viscera MAJOR FUNCTION Movement of a Substance Through the Hollow Organ (By Contraction) i.e., Food through Digestive System TYPE OF CONTROL Involuntary SMOOTH MUSCLE TISSUE STRUCTURAL FEATURES STRIATIONS Absent (Nonstriated, Smooth) Means Sarcomeres Absent Thick and Thin Myofilaments Are Present Not Arranged in Sarcomeres (Not as Extensive) Arrangement of Thick and Thin Myofilaments Different (Myofilaments Criss-cross and Attach to Sarcolemma) SMOOTH MUSCLE TISSUE STRUCTURAL FEATURES NUCLEUS 1/Cell T TUBULES Absent SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM Present But Poorly Developed (Ca++ Comes In From Outside The Cell) SMOOTH MUSCLE TISSUE METHOD OF CONTRACTION Method of Contraction Depends upon Type of Smooth Muscle Tissue VISCERAL (SINGLE UNIT): SYNCYTIUM/SELF-EXCITING Most Common Type of Smooth Muscle Tissue Contracts Like Cardiac Muscle Tissue SMOOTH MUSCLE TISSUE METHOD OF CONTRACTION Method of Contraction Depends upon Type of Smooth Muscle Tissue MULTI UNIT: INDIVIDUAL CONTRACTION/EXCITED BY NERVE IMPULSES Contracts Like Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Motor Units Present) Example: Arrector Pili Muscles