* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PAIN
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
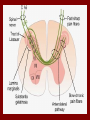
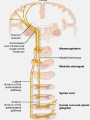
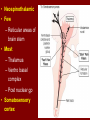
PAIN Dr Ghulam Mustafa LO’s of the class • • • • • • • • • Define pain Properties of pain Stimuli for pain Receptors for Pain Causes of pain Types of pain w.r.t., Site Fast vs Slow pain Pain pathways Body response to pain • Unpleasant sensory experience that is elicited by Noxious or nociceptive stimuli Properties of pain • Pain is a protective reflex • Pain receptors are widely distributed • Commonest symptom • Earliest sign of Morbidity • Non adaptive receptors • Certain viscera insensitive to pain – Brain – Liver parenchyma – Alveoli Stimuli for pain • Mechanical • Thermal – More than 45°C • Chemical – – – – – Bradykinin Serotonin Histamine Potassium ions Proteolytic enzymes Receptors for Pain 1. Superficial skin layers 2. Internal tissues • Periostium • Joint surfaces • Arterial walls • Falx and tentorium Causes of pain 1. Tissue damage • Bradykinin • Increased Potassium • Increased Proteolytic enzymes Rate of tissue damage α Pain intensity 2. Tissue Ischemia • Lactic acid by Anerobic metabolism • Bradykinin and proteolytic enzymes Causes of pain 3 Muscle spasm • Stimulate mechanosensitive pain receptors – Compress the blood vessels and cause ischemia – Increases the rate of metabolism Types of pain w.r.t., Site 1. Cutaneous pain • Skin and subcutaneous tissues • Accurately localized 2. Deep somatic pain • Muscles, Tendons, Joints, Ligaments • Mechanical forces, Ischemia, Chemicals 3. Visceral pain • Poorly localize, radiates or refers • Associated with ANS dysfunction • Rigidity & tenderness nearby skeletal muscles • Fast pain – – – – Sharp pain Pricking pain Acute pain Electric pain • Stimuli – Mechanical – Thermal – Electrical • Transmission – A Delta Fibres • Slow Pain – – – – Burning pain Ache Throbbing pain Chronic pain • Stimuli – Chemical • Transmission – Type C fibres • Transmission velocity – 6 to 30 m/s • Perception time – 0.1 sec after stimulation • Body parts involved – Usually skin • Duration – Short • Neurotransmitter – Glutamate • Transmission velocity – 0.5 to 2 m/s • Perception time – 1 sec or more • Body parts involved – Skin and deep tissues • Duration – Long • Neurotransmitter – Substance P • Localized • • • • • Examples of stimuli Needle prick Skin cut Burn Electric shock • Neo spino thalamic tract • Diffuse • Tissue destruction • Paleo spino thalamic tract • A Delta fibres • Terminate in Lamina I Lamina Marginalis • Excite 2nd order neurons • Cross to opp side thru Ant commissure • Pass upward in Anterolateral pathway • Type C fibres • Terminate in Lamina II & III substantia gelatinosa • Signals thru short fibre neurons • Reach Lamina V • Last neuron give rise to long axons • Cross to opp side thru Ant commissure • Pass upward in Anterolateral pathway • Neospinothalamic • Few – Reticular areas of brain stem • Most – Thalamus – Ventro basal complex – Post nuclear gp • Somatosensory cortex • Paleo spino thalamic – Reticular areas of medulla and pons – Tectal area of mesencephalon – Peri aqueductal gray region • From brain stem – Intra laminar nuclei – V/L Nuclei of thalamus – Hypothalamus Body response to pain • Motor reaction: – Withdrawl reflex – Muscle rigidity • Autonomic reaction – Mild pain • Posterior hypothalamic nuclei –Increased sympathetic discharge –Tachycardia –Increased Blood pressure • Severe pain • Anterior hypothalamic nuclei –Increased Para sympathetic discharge –Bradycardia –Decreased Blood pressure • Emotional reactions – Anxiety – Depression – Crying LO’s were • • • • • • • • • Define pain Properties of pain Stimuli for pain Receptors for Pain Causes of pain Types of pain w.r.t., Site Fast vs Slow pain Pain pathways Body response to pain