* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care
Poliomyelitis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Cysticercosis wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Swine influenza wikipedia , lookup
Anthrax vaccine adsorbed wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
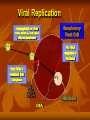
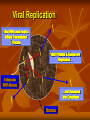
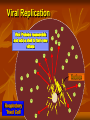
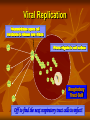
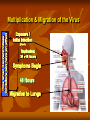
Influenza 2013 - 2014 Gregory Gahm, MD Epidemiology How significant is influenza - really? Influenza Epidemiology The Influenza Virus Getting Infected… Viral Replication Viral Replication Viral Replication Viral Replication Multiplication & Migration of the Virus Preventive Medicine How do I stay healthy? The best way to prevent flu is to GET VACCINATED!!! - unless: You’ve had a documented serious reaction to a previous dose You’ve had Guillain-Barre associated with the vaccine Few Side Effects Most common → redness, soreness or swelling at injection site (Bravo! for your immune system!) Less common → fever and body aches Egg allergy is not a contraindication – esp with a new recombinant vaccine made without any eggs used in the process Recipe for Making a Flu Vaccine AKA: Why you can’t get the flu from the vaccine Making a Vaccine – Step 1 Inoculate eggs with the virus Making a Vaccine – Step 2 Incubate until egg is full of live virus Making a Vaccine – Step 3 Separate virus from egg, discard egg Making a Vaccine – Step 4 Thoroughly KILL virus (chemically, multiple times) Making a Vaccine – Step 5 Chop KILLED virus into small pieces Making a Vaccine – Step 6 Discard the killed RNA Making a Vaccine – Step 7 Put remaining viral shell pieces with Hs & Ns into vaccine Benefits of being vaccinated The ACIP recommends Universal Vaccination (everyone >6 months old) For NH residents the vaccine reduces the risk of: Hospitalization by 50% Pneumonia by 60% Death and complications related to flu by 75-80% In kids / young adults, it is 70-90% effective in preventing flu (also keeps them from spreading it to sibs, parents and our patients) Flu Vaccines for 2013-14 Viral Strains A/California/7/2009 (H1N1) A/Victoria/361/2011 (H3N2) B/Massachusetts/2/2012 +/- B/Brisbane/60/2008 Vaccines Available LAIV (FluMist; 2 – 49 yo) – Quadrivalent Tri - & Quadri - valent inactivated vaccine (IM) High Dose Fluzone (over 65) Intradermal Fluzone (ages 18-64) RIV3 = Recombinant, egg-free vaccine for persons 18 – 49 yo High Dose Fluzone For ages >65 only Contains 4X the antigen for each of the 3 viral strains Only 20-25% of frail elderly (NH pts) develop protective antibodies with the normal seasonal vaccine Non-serious adverse events were more frequent Pain at injection site Muscle aches Redness / swelling at injection site Headache Low-grade fever Malaise Serious adverse event rates were equivalent How do I stay healthy? Avoid close contact with people who are sick Stay home when you are sick Cover mouth & nose when coughing / sneezing Cover mouth & nose when someone else coughs or sneezes! Wash your hands and practice other good, common sense health habits VENTILATE! Open doors & windows on nice days! Clinical Medicine Influenza Recognition and Treatment Influenza A Respiratory Virus NOT the ‘stomach’ flu Spread by coughing and sneezing Symptoms… AKA… How do you know if a patient has the flu? 2 Major Symptoms: Sudden onset of HIGH Fever and/or a Nonproductive Cough LTCFs: watch for multiple cases in a short period of time Other common symptoms: Muscle aches – often profound Sore throat or nasal congestion Headache Confusion or Delirium Rapid Testing Problems with collecting / sending swabs Misses H1N1 Antiviral Treatment If you think someone has the flu: Involve the provider as soon as there are symptoms! Meds only work if started <48 hours from start of symptoms When in doubt, start treatment – STAT – based on clinical judgment STAY HOME or cohort sick patients in LTCFs! Plenty of rest, fluids, nutrition Treat muscle aches / fever with NSAIDs, ASA, Tylenol Cough / lethargy can last 2 – 3 weeks depending on frailty Infectious from 1-2 days before symptoms start until 1-2 days after coughing stops CDPHE Mandatory Vaccination in LTC General Provisions Healthcare entities and workers have a shared responsibility to prevent spread of infection and avoid causing harm to their patients or residents by taking reasonable precautions to prevent the transmission of vaccine-preventable diseases. Vaccine programs are, therefore, an essential part of infection prevention and control for slowing or stopping the transmission of seasonal influenza viruses from adversely affecting those individuals who are most susceptible. Definitions Employee: any person who performs a service for wages or remuneration, including students, trainees, persons who have individual contracts with the healthcare entity, physicians with staff privileges and allied health professionals with privileges. Does not include volunteers or persons who provide services through a contractual arrangement between the licensee and a separate organization, association or other healthcare entity. Definitions Healthcare Worker: any person, working in a facility who has the potential for exposure to patients, residents or consumers of the entity and/or to infectious materials, including body substances, contaminated medical supplies and equipment, contaminated environmental surfaces or air. Includes, but is not limited to physicians, nurses, CNAs, therapists, techs, EMTs, dental personnel, pharmacists, lab personnel, students, trainees, contractual personnel, and persons not directly involved in patient care (eg, clerical, dietary, housekeeping, laundry, security, maintenance, billing and chaplains) Definitions Influenza Season: November 1 through March 31 Proof of Immunization: A written statement from a licensed healthcare provider who has administered a flu vaccine to a healthcare worker Vaccination Targets to be Exempt from Masks % of Employees Vaccinated by Dec 31 2012 60% 2013 75% 2014 90% Other Requirements to be Exempt from Masks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Have defined procedures to prevent spread of flu from unvaccinated workers Maintain documentation for 3 years Report vaccination to CDPHE by March 31 Provide vaccine for each healthcare worker Have a written policy regarding vaccination of your healthcare workers that addresses: Proof of immunization, or A signed medical exemption Maintain proof of annual immunization for employees Inform other healthcare workers who provide services on the premises that you have these policies, require them to be immunized or wear a mask, and you can provide the mask. Masks Each healthcare worker without proof of immunization must wear a surgical or procedure mask during flu season when in direct contact with patients and in common areas.