* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review- Pathway of blood flow through the
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
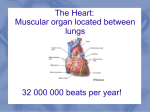
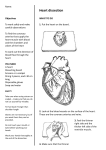
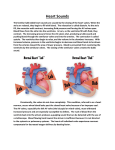
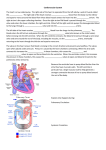
Review- Pathway of blood flow through the Blood from upper body Deoxygenated blood from rest of body to right atrium via superior and inferior vena cava right atrium right ventricle pulmonary artery lung where blood picks up O2 left atrium via pulmonary veins left ventricle oxygenated blood left heart via aorta to rest of the body Blood from lower body https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KSbbDnbSEyM Heart Trivia- Whiteboard activity 1. Label AD in the diagram below. 2. Which kind of blood (deoxygenated/oxygenated?) that entering: a. superior vena cava b. pulmonary vein c. pulmonary artery d. aorta 3. Where does the blood come from before entering the superior vena cava? 4. Where does the blood come from before entering the inferior vena cava? 5. Where does the blood go to after leaving the pulmonary artery? 6. The part receives blood from lung is: a. left ventricle c. left atrium b. right atrium d. septum Tissues of the Heart • The heart is surrounded by twolayered membrane called the pericardium - Epithelial tissue called endocardium, a smooth lining inside the chambers - Muscle tissue called myocardium, that provides the propulsive force Endocardium of atrium end = endothelial cell nuclei Endo = endocardium Myo = myocardium Low power view of ventricle epicardium ad = adipose tissue bv = blood vessel nv = nerve Myo = myocardium Image s from http://courseweb.edteched.uottawa.ca/medicinehistology/English/Cardiovascular/HistologyHeart.htm#Fig 03 The Heartbeat Cardiac cycle = contractions and relaxations of heart muscles in a complete heartbeat Takes ~0.8 s 4 Valves •flaps of connective tissue •prevent backflow Atrioventricular (AV) valves -are tricuspid valve made of 3 flaps and bicuspid (mitral) valve made of 2 flaps - Prevents backflow into atria when ventricles contract “lub” Semilunar valves (both pulmonary and aortic valves; half-moon shape) prevent backflow into ventricles while they relax “dub” Blood flow through valves: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rguztY8aqpk Heart sound: “Lub-dub, lub-dub” •Heart sounds are caused by the closing of valves “Lub” “Dub” recoil of blood recoil of blood against closed AV against closed valves semilunar valves Heart murmur: defective valves causing hissing sound when blood squirts backward through valves Lub-dub with Bill Nye: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=riDPxasIz_I How the heart contracts How the heart contracts: Sinoatrial (SA) node: • Pacemaker, in the wall of right atrium • Sends out electrical signal causing two atria to contract simultaneously Atrioventricular (AV) node • transmits signal through specialized fibres called bundle of His and Purkinje fibres •Purkinje fibres initiate almost simultaneous contraction of all cells of the right and left ventricles https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bwBM2Pa1LA8 with Bill Nye. Watch all Electrocardiograph: records electrical impulses by a beating heart • P wave = atrial contractions • QRS wave = ventricular contractions • T wave = ventricle recovers The “LUB” “DUB” of Our Hearts! “lub” “dub” LUB 1 2 3 DUB 4 the ventricles relax and the semilunar valves close to produce the second heart sound (“DUB”). The relaxation of the ventricles is followed by the next firing of the SA node for the next heartbeat. 5 MRI- imaging tool for the heart Heartbeat in real time https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G4dFVeP9Vdo 14 Blood Pressure • Blood pressure= force exerted on vessels’ walls as blood flows through them • Pulses = evidence of artery under pressure due to heart’s contraction A digital sphymomanometer measuring blood pressure 1. Inflate the cuff to close off flow to brachial artery 2. Listening to pulse, slowly release air until pulse is heard and read the pressure – Systolic (i.e. pressure when the ventricles contract) 3. Slowly release air until no pulse is heard and then read the pressure – Diastolic (i.e. The pressure when the ventricles relax; heart is at rest) 4. Healthy = 120/80 (units = mmHg) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u6saTO8_o2g Factors affecting Blood pressure • • • • • • • • • • Diameter of blood vessels Volume of blood Physical activity Temperature Body position Age (blood pressure usually increases with age) Stress level Diet Drinking too much alcohol Medication etc. Hypertension (high blood pressure) Too much Na+ in diet causes H2O to enter blood by osmosis increases blood volume increases blood pressure High blood pressure reading: above 140/90 mmHg Stiffer arteries make heart work harder Arteries may rupture leading to stroke, heart attack, kidney damage etc. Resource link: https://www.hypertension.ca/en/ Diagnosis https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IGyeNtZZnrk Bypass surgery: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7PpidBmoA4c (@6min) 18 Heart Bypass surgery Atherosclerosis = Hardening of the arteries Plaque (fat, cholesterol, Ca etc) built up in the artery leading to stroke, heart attack, death Balloon angioplasty https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RwWDOZ9oTP8 Face your partner: name as many songs with “Heart” in their titles as you can