* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart - Quia
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
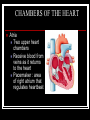
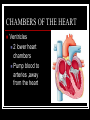
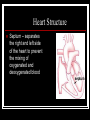
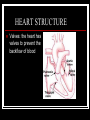
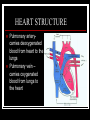
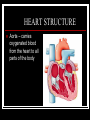
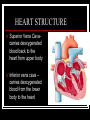
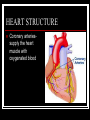
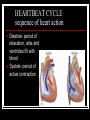
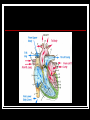
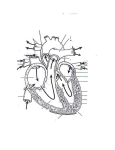
THE HEART THE HUMAN HEART Acts as a pump Is made of muscle (called cardiac muscle) Beats about 70 times a minute Is surrounded by a tough membrane called the pericardium Is divided into 4 chambers CHAMBERS OF THE HEART Atria Two upper heart chambers Receive blood from veins as it returns to the heart Pacemaker : area of right atrium that regulates heartbeat CHAMBERS OF THE HEART Ventricles 2 lower heart chambers Pump blood to arteries ,away from the heart Heart Structure Septum – separates the right and left side of the heart to prevent the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood HEART STRUCTURE Valves: the heart has valves to prevent the backflow of blood HEART STRUCTURE Pulmonary arterycarries deoxygenated blood from heart to the lungs Pulmonary vein – carries oxygenated blood from lungs to the heart HEART STRUCTURE Aorta – carries oxygenated blood from the heart to all parts of the body WARNING! The next slide is a little gory!!! HEART STRUCTURE Superior Vena Cavacarries deoxygenated blood back to the heart from upper body Inferior vena cava – carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the heart HEART STRUCTURE Coronary arteriessupply the heart muscle with oxygenated blood HEARTBEAT CYCLE sequence of heart action Diastole- period of relaxation, atria and ventricles fill with blood Systole- period of active contraction BLOOD PRESSURE Is the force exerted by blood on artery walls Systolic pressure force in arteries when ventricles contract Diastolic pressureforce in arteries when ventricles are filling Normal blood pressure is 120/80 HEART SOUNDS “Lub-Dub” Lub – shutting of valves as ventricles contract (valves to atria) Dub- shutting of valves as ventricles relax (valves to lungs and aorta) Malfunctions Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)condition of increased arterial pressure throughout heartbeat cycle, may be caused by stress, diet, smoking, etc. Atherosclerosis (Hardening of the Arteries)narrowing of arteries due to deposits of fatty materials such as cholesterol and along the vessel walls. Less blood (less oxygen) is able to travel through the smaller openings Malfunctions Heart Attack (Myocardial infarction)Damage to heart muscle caused by lack of blood flow (oxygen) due to total blockage of a coronary artery Malfunctions Anemia- blood disorder characterized by decreased amount of RBC or hemoglobin or iron deficiency resulting in a decreased ability to transport oxygen Leukemia- cancer which causes an increased production of nonfunctional white blood cells Malfunctions Sickle Cell Anemia- Genetic disorder causing production of misshapen RBC, sickle-shaped cells carry less oxygen and clump in capillaries Hemophilia- genetic disorder which results in the blood’s inability to properly clot due to missing clotting factors Angina- pain radiating from chest into the shoulder and arm and is caused by reduced blood supply to heart muscle