* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Infective endocarditis wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
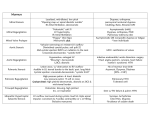
How and why the heart goes wrong RJS What there is to go wrong RJS How and why the heart goes wrong VALVES MUSCLE VESSELS ELECTRICS RJS How and why the heart goes wrong MUSCLE VALVES VESSELS ELECTRICS RJS How and why the heart goes wrong TOO MUCH TOO LITTLE MUSCLE Dilated Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy cardiomyopathy VALVES Stenosed regurgitant VESSELS Blockage aneurysmal ELECTRICS tachycardia bradycardia RJS How and why the heart goes wrong ANATOMIC MOLECULAR INFECTIVE POISON DEGENER. MUSCLE Connections Cardioholes myopathy virus VALVES Malformed floppy bacterial VESSELS Anomalous connections /courses Atheroma blockage ?? Smoking Atheroma instability ?viral drugs ELECTRICS Defective circuitry Drugs, alcohol Stiffening Fibrosis/ calcification fibrosis RJS How and why the heart goes wrong MUSCLE Malformed • connections • holes Cardiomyopathy • hypertrophic • dilated • restrictive Hypertensive disease Remodelling RJS How and why the heart goes wrong VALVES Congenital • malformed Acquired • rheumatic fever • infective endocarditis • trauma • degenerative • floppy • senile calcification RJS Heart Valve lesions • • • • • Mitral stenosis Aortic stenosis Pulmonary stenosis Tricuspid stenosis Prosthetic stenosis • • • • • Mitral regurgitation Aortic regurgitation Pulmonary regurgitation Tricuspid regurgitation Prosthetic regurgitation RJS RJS MS echo RJS Aortic Stenosis - aetiology • Congenital – bicuspid valve • Acquired – Rheumatic – Senile/degenerative RJS Aortic stenosis RJS Echo AS RJS AR - xray RJS AR - Echo RJS How and why the heart goes wrong VESSELS Malformed Atheromatous disease • stenosis narrowing myocardial ischaemia angina • occlusion blockage myocardial infarction • dilatation aneurysmal dissection RJS RJS RJS RJS RJS RJS RJS RJS RJS RJS RJS RJS How and why the heart goes wrong ELECTRICS Malformed • inadequate connection • excessive connection Molecular • instability Degenerative Bystander • MI, infection, cardiomyopathy RJS RJS RJS RJS RJS Sinus node disease RJS AV node disease Complete (3rd degree) heart block RJS What there is to go wrong RJS Atrial flutter RJS Atrial fibrillation RJS What there is to go wrong RJS AV nodal re-entry tachycardia RJS What there is to go wrong RJS Ventricular tachycardia RJS Torsades de Pointes RJS Rhythm Strip During Episode of Sudden Death RJS Implanatable defibrillator in-situ RJS How and why the heart goes wrong ANATOMIC MOLECULAR INFECTIVE POISON DEGENER. MUSCLE Connections Cardioholes myopathy virus VALVES Malformed floppy bacterial VESSELS Anomalous connections /courses Atheroma blockage ?? Smoking Atheroma instability ?viral drugs ELECTRICS Defective circuitry Drugs, alcohol Stiffening Fibrosis/ calcification fibrosis RJS RJS How and why the heart goes wrong TOO MUCH TOO LITTLE MUSCLE Dilated Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy cardiomyopathy VALVES Stenosed regurgitant VESSELS Blockage aneurysmal ELECTRICS tachycardia bradycardia RJS Mitral regurgitation – pathophysiology • • • • • Leaking mitral valve LV emptying LV filling LV dilatation LV stretch contractile failure • • • • LA pressure LA stretch Atrial arrhythmia (atrial fibrillation) Thrombo-embolic risk – stroke (cerebrovascular accident) – heart attack (myocardial infarct) RJS Mitral regurgitation – pathophysiology • • • • • Leaking mitral valve LV emptying LV filling LV dilatation LV stretch contractile failure • • • • LA pressure LA stretch Atrial arrhythmia (atrial fibrillation) Thrombo-embolic risk – stroke (cerebrovascular accident) – heart attack (myocardial infarct) valve muscle electrics vessels RJS