* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Anderson Latin Homepage
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Tagalog grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish pronouns wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin conjugation wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Hungarian verbs wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek verbs wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish verbs wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Finnish verb conjugation wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
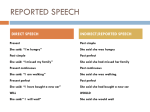
What’s the difference? I. “There is a quiz tomorrow.” II. Mr. Ellis said that there is a quiz tomorrow. 1. Which of these is a direct / indirect statement? 2. How would you characterize an Indirect Statement? When is a Statement Indirect? Indirect Statement occurs when the speaker or writer of a sentence reports what they or another person said, saw, thought, or perceived in any way--without directly quoting that person said, saw, thought, or perceived. Examples in English: 1. I heard that they were not here. 2. Caesar said that the die had been cast. 3. The Romans perceived that the enemies were at the gate. 4. They say that the are hungry. 5. Did you say that you will be prepared for the test? 6. I feel that I’m hungry. How to do this in Latin: The verb of perception or saying conjugates just like any verb. The ‘subject’ or ‘doer’ of the action indirectly being reported goes into the ACCUSATIVE case. The ‘verb’ or action being indirectly reported becomes an INFINITIVE. Why would the verb in the indirect statement NOT be in the indicative mood? The Accusative-Infinitive Construction: Ex 1: Marcus said that his father was working. Marcus dixit patrem laborare. Note that patrem (the ‘subject of the indirect statement) is in the Accusative case where as ‘working’ becomes an infinitive because it is the reported action. “Dixit” declines because it is the action of the sentence (or the main verb) Verbs of Mind or Mouth (M & M) 1. audio 2. sentio 3. video 4. nosco 5. cognosco 6. dico 7. scio 8. puto 9. arbitror 10. intellego 11. nuntio 12. spero 13. nego 14. minor 15. polliceor 16. existimo 17. arbitror 18. oro 19. can(t)o 20. iuro 21. video (that) How to translate the Accusative/Infinitive in Indirect Discourse 1. Trojanos pervenire audivit. S/he heard that the Trojans were arriving. ‘Trojanos’ is the Accusative SUBJECT of an indirect statement. You should almost always try to get a ‘THAT’ into your translation of an indirect statement. Infinitives (like participles) Express Relative Time Perfect Infinitives happened before the main verb. Present Infinitives happen at the same time as the main verb. Future Infinitives happen subsequent the main verb. Infinitive Formation Active Perfect Perfect Stem + Present 2nd Principal Part Future Future Act Partic + -isse esse Passive 4th Princ Part + esse 2nd PP minus ‘e’ or ‘ere’ (3rd conj) + Rare: Fut Act Partic + iri i