* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pronoun Case
Nominative determinism wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sloppy identity wikipedia , lookup
Relative clause wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian declension wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Singular they wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Bound variable pronoun wikipedia , lookup
Third-person pronoun wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
English grammar wikipedia , lookup
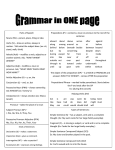
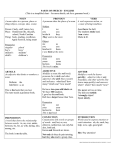
Pronoun Case Her smacked he. Her smacked he. Determining which form of a pronoun to use is a matter of determining how the pronoun is functioning in the sentence and then putting it in the proper form. Is it a subject? An object? Indicating possession? Subject: Who/what is doing the action? Object: Who/what is being acted upon? (this can be direct or indirect object or the object of a preposition) Finding subjects and objects Her smacked he. Subject: The one doing the action. Verb: Object: The action The one being acted upon. Next… Once you have determined whether a pronoun is functioning as a subject or an object, put it in the proper form. Her smacked he. Becomes… She smacked him. Subject-- Object-- Nominative Form Objective Form Pronoun Forms Nominative or Subjective: Used when pronoun is a subject. Objective: Used when pronoun is an object. Possessive: Used when the pronoun is indicating possession. Reflexive: Used in place of the objective when subject and object are identical. Examples Nominative: Al and I are going to the circus. Objective: The bus will take Al and me to the circus. Possessive: My friend Al is going to the circus. (before noun) That Eggo is mine. (used alone) Reflexive: I brought myself to the circus. Singular Pronoun Forms First Person: (n, o, pn pa, r) I, me, my mine, myself Second Person: You, you, your yours, yourself Third Person: He, him, his his, himself She, her, her hers, herself It, it, its its, itself Plural Pronoun Forms First Person: We, us, our ours, ourselves Second Person: You, you, your yours, yourselves Third Person: They, them, their theirs, themselves Special Cases Interrogative Pronoun: WHO Nominative: Who is going to the circus? Objective: With whom are you going? Possessive: Whose circus is better? (noun) Those pies are whose? (alone) Special Cases Use the possessive form of a pronoun before a gerund. Gerund: Verb ending in –ing that functions as a noun Her juggling is masterful. She didn’t mind my asking about her training. Incomplete Constructions A pronoun following than or as in an incomplete construction is the same case as it would be if the construction were completed. Examples: Inc: Jeff is better at baking than (she, her). Comp: Jeff is better at baking than (she, her) is. Inc: The odor upset me as much as (he, him). Comp: The odor upset me as much as it upset (he, him). Practice Using different pronouns for each, write three sentences for each of the pronoun cases: Nominative Objective Possessive Reflexive In your sentences be sure to demonstrate your understanding of gerunds and who/whom.