* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
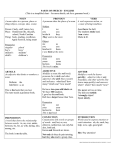
Download Parts of Speech Nouns (SN) – person, place, thing or idea Verbs (V
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish pronouns wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Dutch grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Parts of Speech Nouns (SN) – person, place, thing or idea Verbs (V) – show an action, always in motion. Tells what the subject does. (ex: sit, stand, walk, think) Adverb (Adv) – modifies a verb, adjective or another adverb. Ask, “HOW? WHEN? WHERE?” Adjective (Adj) – modifies a noun or pronoun. Ask, “WHAT KIND? WHICH ONE? HOW MANY?” Article Adjective (A) – a, an, the Conjunction (c) – and, or, but Possessive Noun (PNA) – shows ownership. Ask WHOSE? (ex: Tommy’s) Interjection (I) – shows emotion (ex: Wow!, Great!) Pronoun – takes the place of a noun Subject Pronoun (SP) – I, We, He, She, It, They, You Possessive Pronoun Adjective (PPA) My, Our, His, Her, Its, Their, Your Kinds of Sentences Declarative (D) – makes a statement. Imperative (Imp) – gives a command. Interrogative (INT) – asks a question? Exclamatory (E) – expresses strong feelings Prepositions (P) – connects a noun or pronoun to the rest of the sentence aboard along behind but during into outside through until about among below by except like out to up above across around as beneath beside concerning for from near of over past toward under upon with after against at before between beyond despite down in Inside off on since throughout underneath within without The object of the preposition (OP) – is a NOUN or PRONOUN and answers WHAT? Or WHOM? – comes AFTER the preposition Prepositional Phrase – marked inside parenthesis. Starts before the P and ends after the OP Ex: (during the concert) Helping Verbs (HV) Am Has May is have can are was were be had do does did could would should shall being been might must will Types of Sentences: Simple Sentence (S) – has a subject, verb and is a complete thought. (Ex: My aunt cooks for her large family everyday) Fragment (F) – is missing a subject, or verb and is not a complete thought (Ex: Cooks for her large family everyday.) Simple Sentence Compound Subject (SCS) Ex: My sister and brother played in the pool. Simple Sentence Compound Verb (SCV) Ex: Curtis waved and ran into the house.